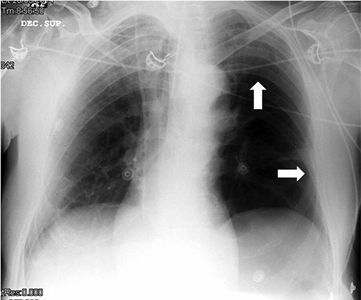
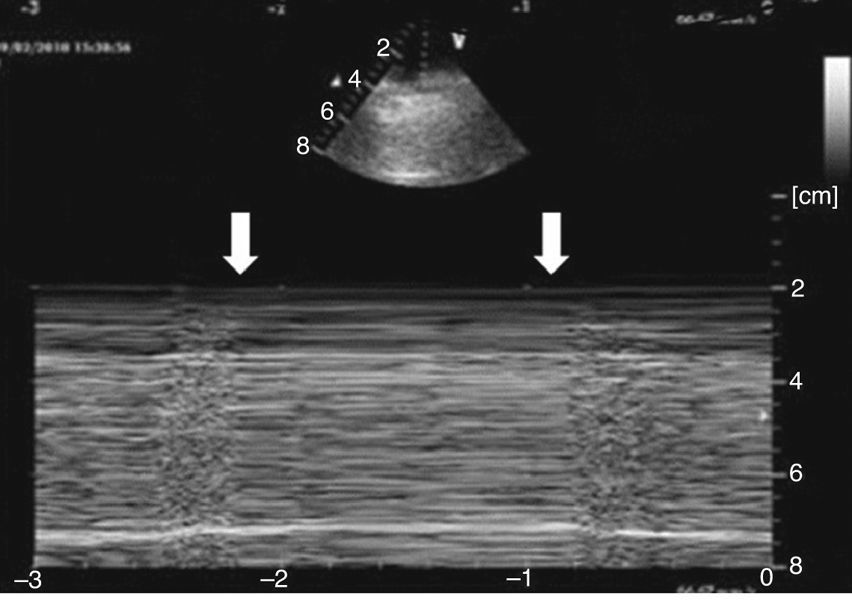
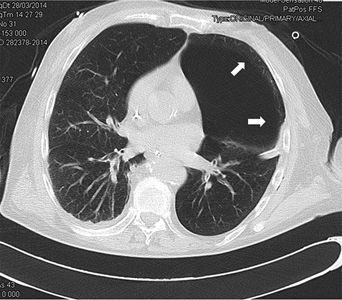
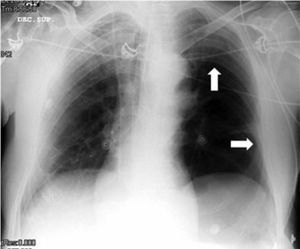
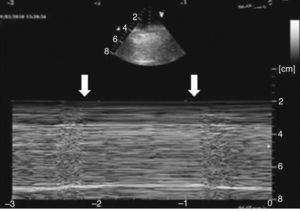
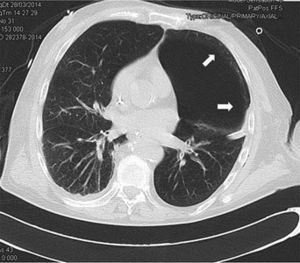
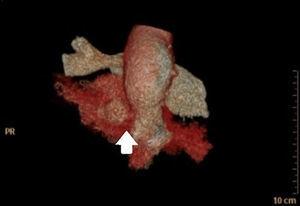
Varón de 71 años con criterios de EPOC grave (FEV1 38%), que ingresa en la UCI por insuficiencia respiratoria hipoxémica grave secundaria a infección respiratoria iniciándose antibioterapia empírica, tratamiento broncodilatador y ventilación mecánica invasiva. En la radiografía de tórax tras intubación (fig. 1) se objetiva imagen compatible con neumotórax izquierdo y se coloca tubo de tórax lateral sin fuga evidente, por lo que realizamos ecografía con signos de persistencia del neumotórax: líneas A, punto pulmonar (fig. 2) y ausencia de deslizamiento pleural. Ante la duda clínica se solicita TC torácica (fig. 3) en la que se identifica una imagen radiolucente redondeada de 10×8,5cm con pared fina sugestiva de ampolla anterior, sin línea clara de neumotórax. En pacientes con enfisema bulloso la ecografía pulmonar puede perder especificidad en el diagnóstico de neumotórax.
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2022
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more