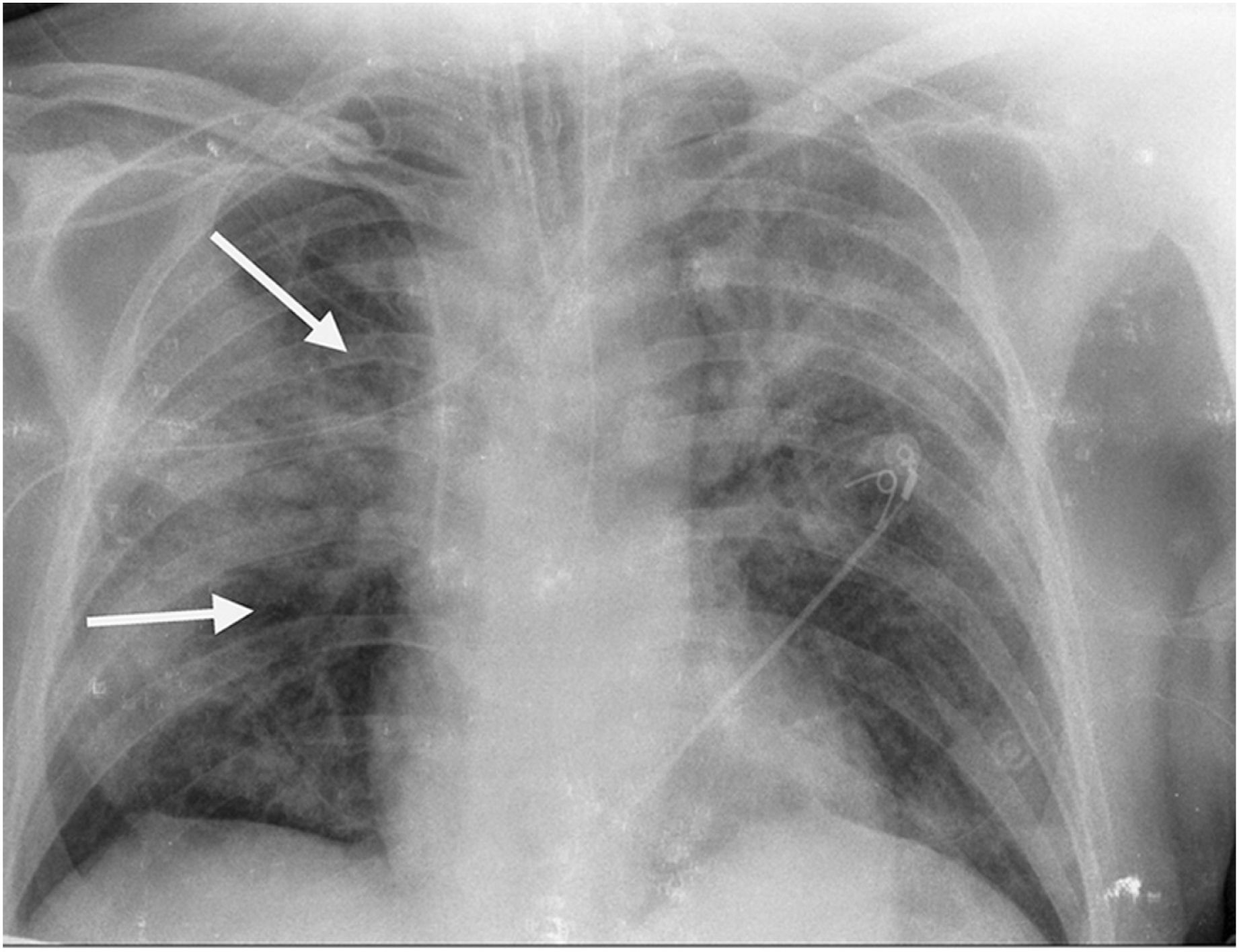
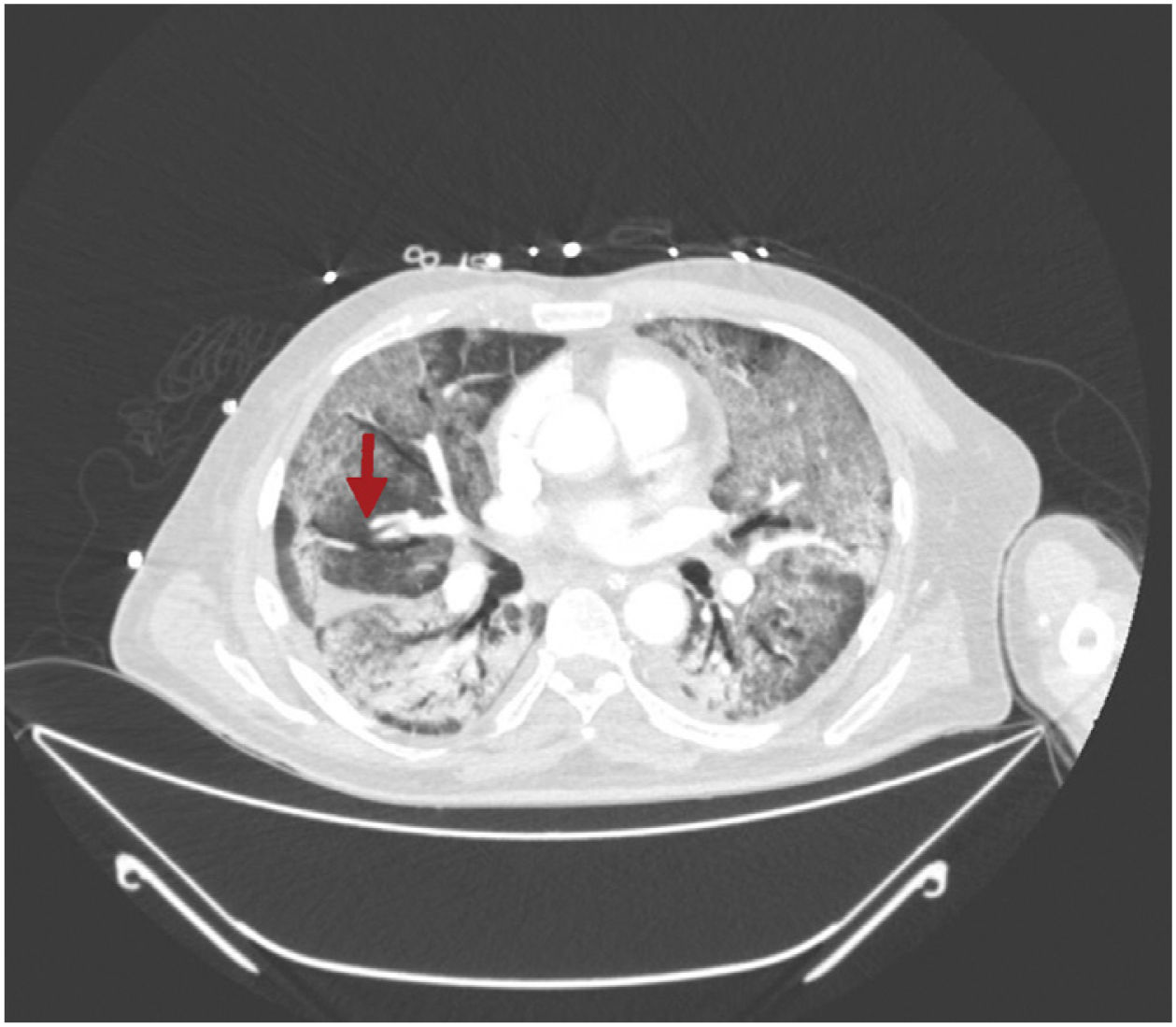
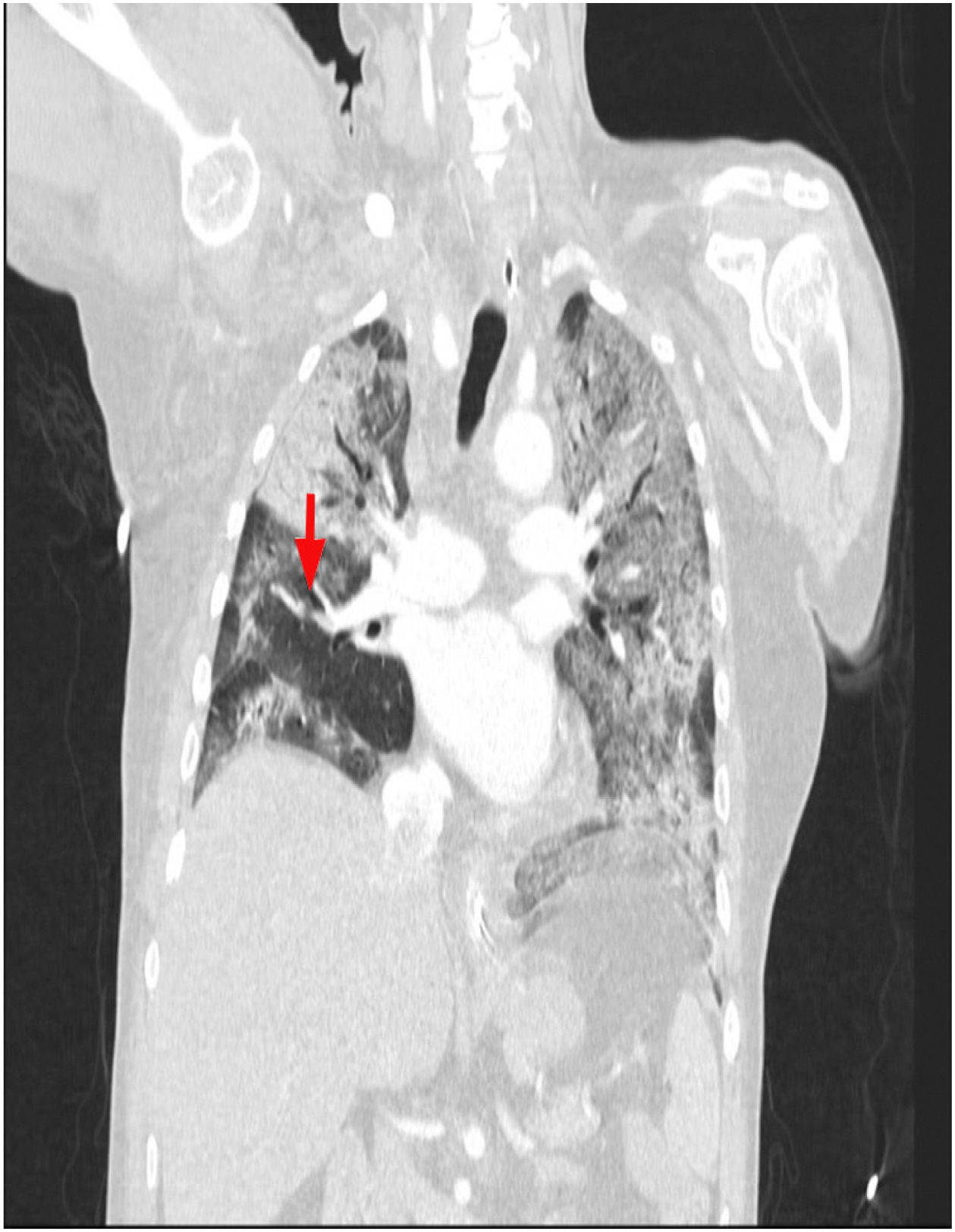
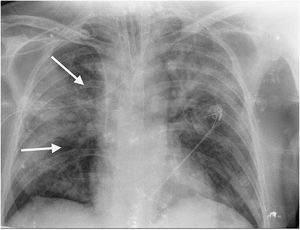
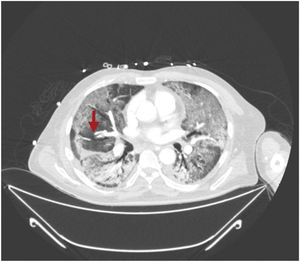
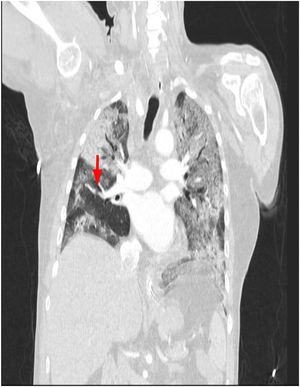
This is the case of a 64-year-old man with a past medical history of hypertension admitted to the ICU with a diagnosis of severe ARDS due to COVID-19-related bilateral pneumonia. The thoracic x-ray reveals a bilateral alveolar-interstitial pattern with damage to the right lung, especially the mid field (Fig. 1, pointer arrows). The blood test results show very high D-dimer levels (28970ng/mL) and due to suspected PTE, a thoracic echocardiography is performed that reveals the presence of RV pressure overload with positive McConnell sign. Following the echocardiographic findings, anticoagulant therapy with low-molecular weight heparin (enoxaparin 1mg/kg/every 12h) is initiated. A thoracic CCTA was performed for diagnostic confirmation purposes that revealed the presence of a repletion defect in the artery of the medial lobe lateral segment (arrows in Figs. 2 and 3) in the PTE setting. Also, the presence of diffuse bilateral damage and extensive areas of cobblestone pattern in a viral infectious process setting (Figs. 2 and 3). The patient remained on anticoagulant therapy until hospital discharge without any associated bleeding complications.
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more