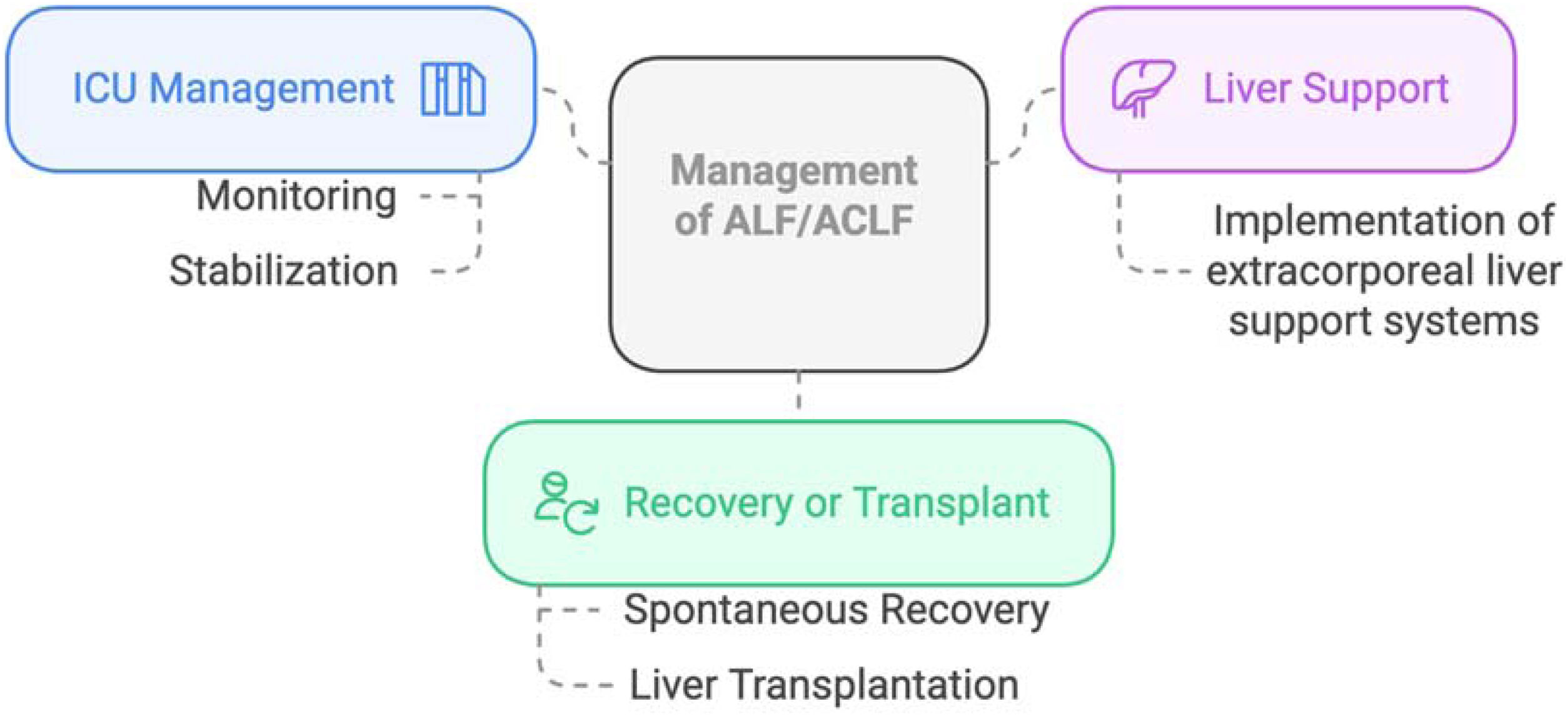
Liver failure, either acute (ALF) or acute-on-chronic (ACLF), is characterized by hepatocellular dysfunction, systemic inflammation, and multiorgan failure, leading to high mortality without liver transplantation (LT). However, LT is limited by organ shortages and medical contraindications, necessitating alternative therapeutic strategies.
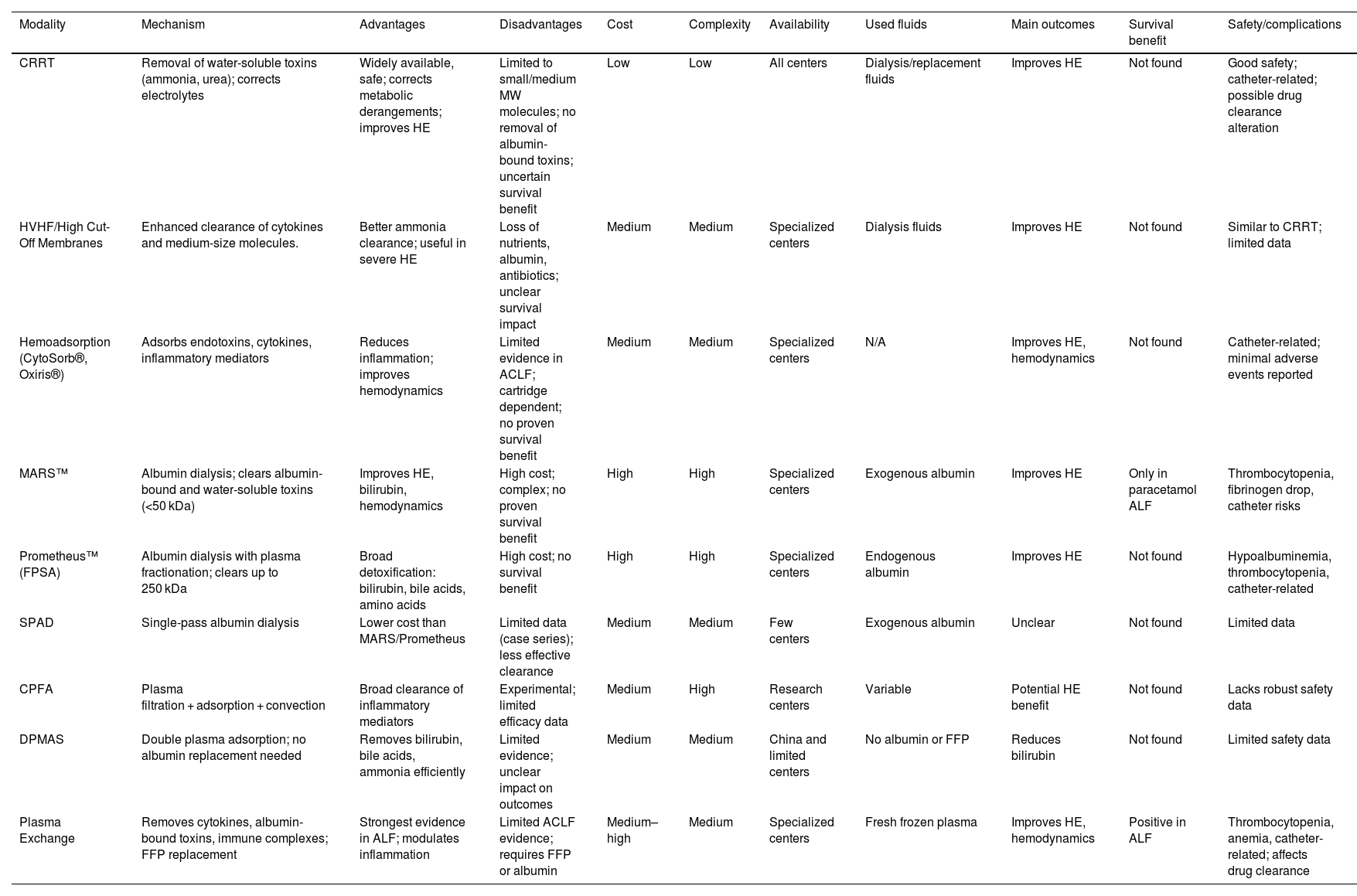
Biological liver support systems, incorporate functional hepatocytes to partially restore hepatic metabolic functions, though clinical trials have not demonstrated a survival benefit. Artificial systems, such as albumin dialysis (MARS, Prometheus), facilitate toxin removal, though evidence remains limited.
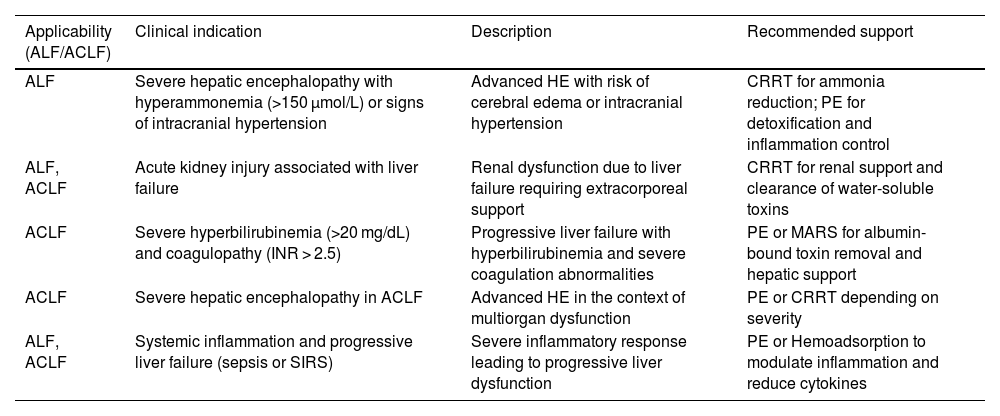
Continuous renal replacement therapy, while not specific for liver failure, is essential in patients with severe hyperammonemia or acute kidney injury, aiding in ammonia clearance and fluid balance control.
Plasma exchange (PE) has promising detoxification and immunomodulatory effects, improving survival in ALF. In ACLF, PE may reduce systemic inflammation, though evidence remains limited.
Further studies are needed to optimize ECLS therapies, refine patient selection, and establish their role in ALF and ACLF management.
La insuficiencia hepática, ya sea aguda (IHA) o aguda sobre crónica (ACLF), se caracteriza por disfunción hepatocelular, inflamación sistémica y fallo multiorgánico, con una alta mortalidad en ausencia de trasplante hepático (TH). Sin embargo, el TH está limitado por la escasez de órganos y contraindicaciones médicas, lo que ha motivado el desarrollo de terapias de soporte extracorpóreo. Los sistemas de soporte hepático biológico, diseñados para restaurar funciones metabólicas mediante hepatocitos funcionales, no se utilizan actualmente en la práctica clínica. Entre los sistemas artificiales, técnicas como MARS y Prometheus permiten la eliminación de toxinas unidas a albúmina, aunque su uso ha disminuido y no han demostrado beneficio en la supervivencia. La terapia de reemplazo renal continua es útil en pacientes con hiperamoniemia o lesión renal aguda. El intercambio plasmático ha demostrado beneficios en la IHA y podría tener un rol en el ACLF. Se requieren estudios para definir su papel clínico.
Article
Go to the members area of the website of the SEMICYUC (www.semicyuc.org )and click the link to the magazine.