Sepsis remains a major cause of mortality worldwide. While neutrophil CD64 (nCD64) has demonstrated superior performance in detecting sepsis compared to conventional biomarkers, its prognostic value remains unclear. This meta-analysis evaluates the performance of nCD64 in predicting mortality in patients with sepsis.
DesignSystematic review and meta-analysis.
SettingsA systematic search of PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science was conducted up to January 28, 2025, to identify relevant studies.
PatientsPatients aged 16 years or older diagnosed with sepsis based on Sepsis-1, Sepsis-2, or Sepsis-3 criteria.
InterventionsStudies assessing the predictive accuracy of nCD64 for mortality and providing sufficient data for contingency table construction were included.
Main variables of interestPooled sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) were calculated with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Overall predictive accuracy was assessed using the area under the summary receiver operating characteristic curve.
ResultsEight studies involving 756 patients were included. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, and DOR of nCD64 for predicting mortality were 0.79 (95% CI: 0.68–0.87), 0.67 (95% CI: 0.56–0.77), and 7.71 (95% CI: 4.38–13.57), respectively. The predictive accuracy was 0.80.
ConclusionsOur findings suggest that nCD64 may serve as a valuable auxiliary biomarker for identifying patients with sepsis at higher risk of mortality.
La sepsis sigue siendo una de las principales causas de mortalidad en todo el mundo. Aunque el CD64 de los neutrófilos (nCD64) ha demostrado un rendimiento superior en la detección de la sepsis en comparación con los biomarcadores convencionales, su valor pronóstico sigue sin estar claro. Este metaanálisis evalúa el rendimiento del nCD64 en la predicción de la mortalidad en pacientes con sepsis.
DiseñoRevisión sistemática y metaanálisis.
ÁmbitoSe realizó una búsqueda sistemática en PubMed, Embase, la Biblioteca Cochrane y Web of Science hasta el 28 de enero de 2025 para identificar estudios relevantes.
Pacientes o participantesPacientes de 16 años o más diagnosticados con sepsis según los criterios de Sepsis-1, Sepsis-2 o Sepsis-3.
IntervencionesSe incluyeron estudios que evaluaron la precisión predictiva del nCD64 para la mortalidad y que proporcionaron datos suficientes para la construcción de una tabla de contingencia.
Variables de interés principalesSe calcularon la sensibilidad, la especificidad y la razón de probabilidades diagnóstica (DOR) agrupadas con un intervalo de confianza (IC) del 95%. La precisión predictiva general se evaluó utilizando el área bajo la curva resumen de las características operativas del receptor.
ResultadosSe incluyeron ocho estudios con un total de 756 pacientes. La sensibilidad, la especificidad y la DOR agrupadas del nCD64 para predecir la mortalidad fueron 0.79 (IC del 95%: 0.68–0.87), 0.67 (IC del 95%: 0.56–0.77) y 7.71 (IC del 95%: 4.38–13.57), respectivamente. La precisión predictiva fue de 0.80.
ConclusionesNuestros hallazgos sugieren que el nCD64 podría servir como un biomarcador auxiliar valioso para identificar a los pacientes con sepsis con mayor riesgo de mortalidad.
Sepsis is a complex syndrome characterized by physiological, pathological, and biochemical abnormalities triggered by infection.1 Although age-standardized incidence and mortality rates have declined, sepsis remains a significant global public health concern and a leading cause of health loss.1,2 Evidence suggests that early detection and prompt, appropriate treatment are crucial in determining patient outcomes and reducing mortality.3,4 A major challenge in sepsis management is accurately identifying patients at high risk of death who may benefit from closer monitoring and targeted interventions.4 To enhance patient outcomes, a reliable biomarker or predictor of sepsis-related mortality and morbidity is essential for tracking disease progression and guiding timely clinical decisions.5,6
Over the past decade, extensive research has emphasized the potential of biomarkers in sepsis, making them valuable tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic decision-making.7–10 Among the most widely studied biomarkers, C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin (PCT) have been commonly used in clinical practice, particularly for assessing sepsis diagnosis and prognosis.10–13 More recently, neutrophil cluster of differentiation 64 (nCD64), also known as the high-affinity Fc gamma receptor I (FcγRI), has emerged as a highly sensitive and specific marker for detecting sepsis.14–16
Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs) are cell surface glycoproteins that specifically recognize and bind to the Fc region of immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies.17 By interacting with the constant region of IgG heavy chains, FcγRs serve as a crucial link between humoral and cellular immunity.18 CD64 is the highest-affinity receptor among all FcγRs.19 It is primarily expressed on myeloid cells, including monocytes, macrophages, natural killer cells, and neutrophils.20 Under normal conditions, CD64 is present at low levels on resting neutrophils in healthy individuals.21 However, its expression is significantly upregulated in response to microbial cell wall components such as lipopolysaccharides, complement fragments, and various cytokines, including interferon-γ, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-8 (IL-8), and IL-12.22 Notably, nCD64 expression increases significantly within hours of bacterial infection,23 often rising more than tenfold, enabling clear differentiation between resting and activated neutrophils.24 This rapid and pronounced upregulation has been leveraged as a diagnostic marker, particularly for identifying sepsis.24,25 Additionally, nCD64 expression remains stable after blood collection and requires only a small sample for assessment,24 making it a highly practical tool. Comparative studies evaluating nCD64 alongside other commonly used sepsis biomarkers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), white blood cell count, and IL-6, have demonstrated its superior performance in the early detection of sepsis.15,26,27
Although previous studies have investigated the prognostic value of nCD64 in sepsis,28–32 its role in predicting mortality has not been systematically analyzed and summarized. Therefore, this systematic review aims to assess the utility of nCD64 as a predictor of mortality in patients with sepsis.
Materials and methodsThis systematic review was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; CRD420250652384) and conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.33 Two independent reviewers (S.E. and S.H.Y.) conducted the literature search, selected relevant studies, extracted data, and assessed study quality. Any discrepancies were resolved through discussion.
Search strategy, study selection, and eligibilityA systematic search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science for articles published up to January 28, 2025. The search strategy included the terms "CD64," "sepsis," "mortality," and "prognosis." Detailed search strategies for each database are provided in the Supplementary materials (Table 1S). Studies were included if they evaluated the predictive accuracy of nCD64 in adult patients with sepsis and reported sufficient data to construct a contingency table. Sepsis was defined based on any of the following criteria: Sepsis-1 (1992 ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference definition),34 Sepsis-2 (2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference),35 or Sepsis-3 (2016 Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock).1
No restrictions were placed on the publication date. To identify additional relevant studies, we also screened the reference lists of eligible articles. However, we did not search trial registries or other sources of grey literature such as ClinicalTrials.gov or conference proceedings. Studies were excluded if they did not focus on sepsis or the predictive accuracy of nCD64. Additionally, we excluded reviews, letters, case reports, editorials, guidelines, and in vitro studies. Duplicate publications, studies involving pediatric patients (<16 years), and non-English articles were also excluded.
Data extractionFrom each eligible study, we extracted the following data: first author, year of publication, country, study period, patient characteristics (e.g., age and sex), clinical setting, timing and location of nCD64 measurement, study outcome, inclusion and exclusion criteria, sepsis definition, nCD64 cutoff value, nCD64 measurement units, analytical method, detecting instrument, total number of patients, and the numbers of true positives, false positives, true negatives, and false negatives for nCD64 in predicting mortality.
Risk of bias assessmentTwo independent reviewers (S.E. and S.H.Y.) evaluated the methodological quality of the included studies using the Quality in Prognosis Studies (QUIPS) tool.36 This tool assesses six domains: study participation, study attrition, prognostic factor measurement, outcome measurement, study confounding, and statistical analysis and reporting. Each domain was classified as having a high, moderate, or low risk of bias. Any discrepancies were resolved through consensus. To evaluate the level of agreement between the two reviewers during the selection process, Cohen’s Kappa coefficient was calculated.37 The strength of agreement was interpreted according to the Landis and Koch criteria, where values of 0.61–0.80 indicate substantial agreement, and values above 0.80 indicate almost perfect agreement.38
Statistical analysisWe calculated pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (+LR), negative likelihood ratio (−LR), and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), along with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) using a bivariate random-effects model based on the extracted data. To evaluate overall test accuracy, we determined the area under the summary receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). Heterogeneity among studies was assessed using forest plots, Cochran’s Q test (p < 0.05 indicating significance), and the I² statistic (I² > 50% considered significant) with 95% CIs. In cases of significant heterogeneity, subgroup analyses and univariate meta-regression were performed using the following covariates: geographic region (Asia vs. Europe), measurement setting (intensive care unit [ICU] vs. non-ICU), outcome definition (28-day mortality vs. other mortality measures such as in-hospital or ICU mortality), sepsis definition (Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS)-based [Sepsis-1 and Sepsis-2] vs. Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score-based [Sepsis-3]), and detection instrument (Beckman Coulter FC500 vs. others). To prevent double-counting bias, only one dataset was selected when multiple datasets from the same study population were available. If a study reported multiple cutoff values within the same population, only the dataset using a single cutoff value for nCD64 was included in the analysis. Publication bias was assessed using Deeks’ funnel plot, with p < 0.1 indicating potential bias. Statistical analyses were conducted using STATA version 18.0 (StataCorp, College Station, Texas) with the MIDAS and Metandi modules. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
ResultsThe initial search yielded 221 titles and abstracts, including 49 from PubMed, 87 from Embase, 4 from the Cochrane Library, 58 from Web of Science, and 23 from other sources, such as reference list screening. After removing 84 duplicates, 137 articles remained for screening. Based on the eligibility criteria, 108 articles were excluded (Fig. 1). Among the 29 full-text articles reviewed, 18 lacked sufficient data to construct a 2 × 2 contingency table, two did not primarily focus on patients with sepsis, and one included pediatric patients. Ultimately, 8 studies15,28,39–44 comprising 756 patients were included in the final analysis (Fig. 1). Cohen’s Kappa coefficient was 0.74 for title and abstract screening, and 0.78 for full-text eligibility assessment, which is interpreted as substantial agreement.
Study characteristicsThe characteristics and diagnostic criteria of the studies included in this meta-analysis are summarized in Table 1 and the Supplementary materials (Table 2S). The selected studies, published between 2006 and 2024, were conducted in Asia and Europe, with two from China, three from Greece, and one each from India, Poland, and Vietnam. Most studies (62.5%) were conducted in ICUs. Flow cytometry was the standard method for analyzing nCD64 in all studies, with the Beckman Coulter FC500 (Beckman Coulter, Miami, FL, USA) being the most frequently used detection instrument. The included studies utilized different nCD64 measurement units, including median fluorescence intensity, antibodies bound per cell, absolute counts of CD64-expressing neutrophils, and changes in the percentage of CD64-expressing neutrophils from day 0 to day 8, among others. Mortality outcomes assessed varied among studies, with 28-day mortality reported in 50% of studies, in-hospital mortality in 25%, and ICU mortality in 25%.
Characteristics of the included studies.
| Study id | Country | Place of measurement | Number of patients | Outcome | Sepsis definition | nCD64 measurement units | Cutoffd | Analytical method | Detecting instrument | Time of nCD64 measurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 Livaditi28 | Greece | ICU | 47 | 28-day mortality | Sepsis-1 | MFI | 6,252 | FCM | BD FACSCalibu | During the first 24 h from sepsis onset |
| 2008 Danikas39 | Greece | Intermediate care unit | 31 | In-hospital mortality | Sepsis-1 | MIF | 2.45 | FCM | Beckman Coulter EPICS-XL-MCL | On the day of admission and within 24 h of sepsis onset |
| 2016 Skirecki40 | Poland | ICU | 27 | In-hospital mortality | Sepsis-2 | ABC | 27,117,912 | FCM | BD FACS Canto II | On day 1 of septic shock diagnosis |
| 2019 Xini41 | Greece | NR | 65 | 28-day mortality | Sepsis-2 | Absolute countsa | 2500 cells/mm³ | FCM | Beckman Coulter FC500 | Within 24 h of the first organ failure |
| 2020 Yin15 | China | ED | 151 | 28-day mortality | Sepsis-3 | MFI | 5.45 | FCM | Beckman Coulter FC500 | Upon admission |
| 2023 Pham42 | Vietnam | ICU | 86 | ICU mortality | Sepsis-3 | % Δ nCD64b | − 1.2 | FCM | BD FACS CANTO | Baseline measurement at ICU admission (T0), re-measured at 48 h (T48) |
| 2024 Patnaik43 | India | ICU | 60 | 28-day mortality | Sepsis-3 | % CD64-positive neutrophils | 11% increase from day 0 to day 8 | FCM | BD FACS Canto II | Upon ICU admission |
| 2024 Zhu44 | China | ICU | 289 | ICU mortality | Sepsis-3 | NRc | 1.49 | FCM | Beckman Coulter FC500 | Upon entry to the ICU |
ABC: antibodies bound per cell; CD: cluster of differentiation; ED: emergency department; FCM: flow cytometry; ICU: intensive care unit; MFI: median fluorescence intensity; MIF: mean intense fluorescence; nCD64: neutrophil CD64; NR: not reported; PMNs: polymorphonuclear cells.
The risk of bias assessments for each study are provided in the Supplementary materials (Table 3S). Overall, most studies demonstrated a low or moderate risk of bias. In the study participation domain, six studies (75%) were assessed as having a low risk of bias due to adequate participant inclusion, clearly reported inclusion/exclusion criteria, and a well-described source population. The study attrition and prognostic factor measurement domains each had one study classified as moderate risk due to unclear reporting of missing participants (e.g., losses at follow-up) and ambiguities in measurement methods (e.g., unclear nCD64 measurement units), respectively. All studies were rated as having a low risk of bias in the outcome measurement domain, as they provided well-defined outcome assessments with clear definitions. However, in the study confounding domain, three studies (37.5%) were considered to have a moderate risk of bias, as they lacked sufficient analysis of potential confounding factors that could influence the observed prognostic effect. The statistical analysis and reporting domain was generally assessed as low risk of bias, except for one study, which was rated as high risk due to issues in statistical reproducibility, where some primary outcomes could not be verified using the same analytical approach (Fig.2).
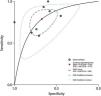
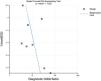
Pooled predictive accuracy of nCD64The forest plots depicting the pooled sensitivity and specificity are presented in Fig. 3. The overall sensitivity estimate was 0.79 (95% CI: 0.68–0.87), and the specificity estimate was 0.67 (95% CI: 0.56–0.77). The pooled estimates for the + LR, –LR, and DOR were 2.42 (95% CI: 1.82–3.22), 0.31 (95% CI: 0.21–0.47), and 7.71 (95% CI: 4.38–13.57), respectively. The AUC was 0.80 (95% CI: 0.76–0.83) (Fig. 4), indicating that nCD64 demonstrates good predictive accuracy for mortality in patients with sepsis. Additionally, Deeks’ funnel plot showed no significant evidence of publication bias (p = 0.20) (Fig. 5).
Statistical heterogeneity across the included studies was assessed using Cochran’s Q test and the I² statistic. Significant heterogeneity and inconsistency were observed for both pooled sensitivity (I² = 65.1%, Chi-square = 20.03, p = 0.01) and pooled specificity (I² = 86.3%, Chi-square = 51.2, p < 0.01). To investigate potential sources of heterogeneity, univariate meta-regression was performed (Table 2).
Stratified meta-regression analyses.
| Parameter | Category | Number of studies | Number of patients | Sensitivity | Specificity | Joint Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pooled value [95% CI] | P | Pooled value [95% CI] | P | LRT Chi-Square | P | I2 | ||||
| Region | Asia | 4 | 586 | 0.82 [0.71−0.93] | 0.68 | 0.62 [0.49−0.75] | 0.06 | 1.59 | 0.45 | 0% |
| Europe | 4 | 170 | 0.74 [0.59−0.90] | 0.74 [0.61−0.87] | ||||||
| Place of measurement | ICU | 5 | 509 | 0.74 [0.65 – 0.84] | 0.01 | 0.68 [0.55−0.82] | 0.88 | 19.71 | <0.01 | 90% |
| non-ICU | 2 | 182 | 0.95 [0.89–1.00] | 0.63 [0.42−0.84] | ||||||
| Outcome | 28-day mortality | 4 | 323 | 0.79 [0.66−0.92] | 0.35 | 0.68 [0.54−0.82] | 0.50 | 0.05 | 0.98 | 0% |
| Othersa | 4 | 433 | 0.78 [0.65 – 0.92] | 0.66 [0.51−0.82] | ||||||
| Sepsis definition | SIRS-based | 4 | 170 | 0.74 [0.59−0.90] | 0.68 | 0.74 [0.61−0.87] | 0.06 | 1.59 | 0.45 | 0% |
| SOFA score-based | 4 | 586 | 0.82 [0.71−0.93] | 0.62 [0.49−0.75] | ||||||
| Detecting instrument | Beckman Coulter FC500 | 3 | 505 | 0.81 [0.67−0.95] | 0.49 | 0.60 [0.46−0.74] | 0.06 | 1.85 | 0.40 | 0% |
| Others | 5 | 251 | 0.78 [0.65−0.92] | 0.73 [0.61−0.84] | ||||||
CI: confidence interval; ICU: intensive care unit; LRT: likelihood ratio test; NA: not available; SIRS: Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
Sensitivity was found to be lower in studies conducted in ICU settings compared to those conducted in non-ICU settings (0.74 vs. 0.95; p = 0.01), suggesting that nCD64 may demonstrate higher sensitivity in non-ICU settings. However, specificity did not significantly differ between ICU and non-ICU settings (p = 0.88). Additionally, no significant difference in sensitivity or specificity were observed based on geographic region, mortality outcome definition, sepsis definition, or detection instrument. Although region, sepsis definition and detection instrument appeared to have a slight influence on specificity (p = 0.06), this did not reach statistical significance.
In the joint model, the measurement setting (ICU vs. non-ICU) was identified as a primary source of heterogeneity (LRT Chi² = 19.71, p < 0.01). The high I² value (90%) further supports the presence of considerable heterogeneity across studies. Other factors, including region, outcome, sepsis definition, and detection instrument, did not significantly contribute to heterogeneity (p-values > 0.05), with I² values of 0, indicating minimal heterogeneity (Table 2).
To complement the meta-regression results, we also estimated the AUC for each subgroup, where statistically feasible. The summary receiver operating characteristic curves and corresponding AUC values are presented in the Supplementary materials (Table 4S and Figs. 1S–7S). AUC ranged from 0.71 to 0.81, indicating fair to good prognostic accuracy.45 Among comparable subgroups, the AUC was slightly higher in studies conducted in Asia (0.80) than in those conducted in Europe (0.77), and in studies using a SOFA score-based sepsis definition (0.80) compared to those using a SIRS-based definition (0.77).
DiscussionThis study evaluated the ability of nCD64 to predict mortality in patients with sepsis. Despite the variability in measurement units across included studies, overall nCD64 demonstrated moderate pooled sensitivity (0.79), low specificity (0.67), and good overall predictive accuracy (AUC = 0.80) for mortality prediction. While an AUC ≥ 0.80 suggests good predictive performance,45 the relatively low specificity may lead to false-positive results, limiting its role as a standalone diagnostic tool. Given its moderate sensitivity, nCD64 may be more useful as a screening tool rather than a confirmatory test, aiding in the early identification of patients with sepsis at high risk of mortality who require close monitoring. For instance, when combined with clinical symptoms or severity scoring systems, nCD64 may serve as a valuable adjunct in assessing mortality risk in sepsis.
Our findings indicate that the place of measurement (ICU vs. non-ICU) is a key contributor to heterogeneity, significantly affecting sensitivity. Sensitivity was lower in studies conducted in ICUs compared to those in non-ICU settings (e.g., emergency departments or intermediate care units). However, given the limited number of studies conducted outside the ICU, these results should be interpreted with caution. Further research is needed to assess the performance of nCD64 across diverse clinical settings beyond the ICU.
The included studies employed different sepsis definitions (SIRS-based [Sepsis-1 and Sepsis-2] vs. SOFA score-based [Sepsis-3]), which may have introduced clinical heterogeneity. To explore the potential impact of these differences, we conducted a subgroup analysis based on the sepsis definition used. Sensitivity was higher in studies using SOFA score-based criteria (0.82 vs. 0.74), whereas specificity was higher in studies using SIRS-based criteria (0.74 vs. 0.62). Although these differences did not reach statistical significance, they suggest a potential trend that may become more apparent as additional studies become available. Additionally, the predictive accuracy was slightly higher in studies using a SOFA score-based sepsis definition (0.80) compared to those using a SIRS-based definition (0.77), although both demonstrated fair to good prognostic accuracy. These findings support the potential utility of nCD64 as a prognostic tool across varying sepsis definitions, though caution is warranted when interpreting the pooled results.
Other covariates, including geographic region, detecting instrument, and outcome did not have a statistically significant impact on sensitivity or specificity. This suggests that nCD64 performance is generally consistent across different study regions, and outcome definitions, and detecting instruments. However, specificity differences related to region and detecting instrument were borderline significant (p = 0.06), suggesting a potential influence that warrants further investigation.
Most included studies reported that nCD64 expression at admission was higher in patients with sepsis who did not survive compared to those who did.15,28,40 Moreover, when measured serially, an increase in nCD64 levels (or % delta nCD64) was associated with higher mortality.42,43 This is consistent with previous findings indicating that nCD64 expression correlates with disease severity.28,46,47 Given its role in the inflammatory response, elevated CD64 levels at admission may reflect sepsis severity, whereas a decline over time could indicate immune regulation and recovery. However, two studies reported conflicting results. Danikas et al.39 observed that increased CD64 expression on polymorphonuclear cells at admission was associated with survival. However, multivariate analysis identified neutrophil phagocytic activity, rather than CD64 expression alone, as the only independent predictor of survival. Additionally, Xini41 reported that an early absolute CD64/CD15/CD45 neutrophil count below 2500/mm³ was independently associated with poor prognosis. These discrepancies may stem from differences in patient characteristics, study design, nCD64 measurement units, and individual variations in immune response.
Tracking serial changes in nCD64 levels can provide valuable prognostic insights in septic patients. Patnaik et al.43 found that an increase in nCD64 levels from the initial measurement to day 8 was a strong independent predictor of 28-day mortality. Similarly, Pham et al.42 reported that monitoring changes in nCD64 levels within the first 48 h of admission could aid in predicting patient outcomes. Their findings showed that nCD64 levels decreased significantly over the first 48 h after ICU admission in survivors, whereas this change was not statistically significant in non-survivors. The AUC value of % delta nCD64 (0.72), defined as [(nCD64 at 48 h − nCD64 at 0 h) / nCD64 at 0 h × 100%], demonstrated greater accuracy compared to delta nCD64 (0.70), the SOFA score (0.70), and the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score (0.68). These results highlight the importance of considering dynamic trends in nCD64 over time, as its kinetic changes may provide critical prognostic information at different stages of sepsis.
Interestingly, Patnaik et al.43 and Yin et al.15 reported that nCD64 demonstrated greater prognostic value than CRP and PCT, both of which are widely used biomarkers in sepsis and septic shock. This finding is consistent with a recent study by Huang et al.,31 which showed that nCD64 exhibited higher predictive accuracy for mortality in patients with sepsis compared to CRP and PCT. The superior performance of nCD64 may be attributed to its direct role in the immune response to infection. Unlike CRP and PCT, which are acute-phase proteins elevated in response to inflammation, nCD64 plays a key role in pathogen recognition, phagocytosis, and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, making it a more specific marker of immune activation in sepsis.39 However, the findings remain somewhat inconsistent. Zhu et al.44 reported that while nCD64 outperformed CRP in predicting outcomes, it was not superior to PCT. These discrepancies highlight the need for further studies to clarify the comparative prognostic value of nCD64, CRP, and PCT in clinical practice.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate nCD64 as a predictive biomarker for mortality in patients with sepsis. However, several limitations should be considered. First, significant heterogeneity was observed in the meta-analysis. Although meta-regression and subgroup analyses identified some potential sources of variability, certain factors remain unexplained. In particular, heterogeneity in the diagnostic criteria for sepsis among the included studies may have contributed to this variability. While some studies adopted SIRS-based definitions (Sepsis-1 or Sepsis-2), others used the SOFA score-based Sepsis-3 definition. This variation may have affected the prognostic performance of nCD64 across studies. Although our subgroup analysis revealed some differences in sensitivity and specificity between these groups, the results were not statistically significant. Moreover, due to the limited number of included studies, we were unable to perform separate analyses for each individual sepsis definition, which restricts a more granular understanding of its impact. Accordingly, the inconsistency in sepsis definitions underscores the need for future studies using standardized diagnostic criteria. Second, we were unable to compare the pooled prognostic accuracy of CRP and PCT against nCD64 due to the limited number of studies providing direct comparative data. Third, most of the included studies did not clarify whether patients measured in non-ICU settings were later transferred to the ICU during their hospital stay, nor did they report information regarding limitations of therapeutic effort (e.g., do-not-resuscitate orders or palliative care). Due to this limitation, we categorized the studies based on the location where nCD64 samples were collected (ICU vs. non-ICU), as this was the most consistently reported information. This approach may have introduced potential bias in the prognostic interpretation of nCD64 values across different patient populations. Fourth, our search was restricted to studies published in English. Although this approach is common in systematic reviews, it may have led to the exclusion of potentially relevant studies published in other languages. Future reviews should consider including non-English publications, which may contribute valuable insights. Finally, variations in nCD64 measurement units across the included studies resulted in inconsistencies in cutoff values. Future research should focus on standardizing nCD64 measurement methods and establishing an optimal cutoff value for clinical use. Therefore, further large-scale prospective clinical studies are needed to address these limitations and validate the prognostic utility of nCD64 in sepsis.
ConclusionsOur findings suggest that nCD64 may serve as a valuable auxiliary biomarker for predicting mortality in patients with sepsis. This study enhances our understanding of the prognostic significance of nCD64 and may offer insights for developing future therapeutic strategies in sepsis management.
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing process*AI technology, ChatGPT (OpenAI, San Francisco, CA, USA), was used only for improving the quality and readability of the language. The authors take full responsibility for the content and interpretation of this manuscript.
FundingThe authors received no financial support for this study.
CRediT authorship contribution statementSeo Hee Yoon: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing - original draft. Sohyun Eun: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing - review & editing.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this manuscript.
None.