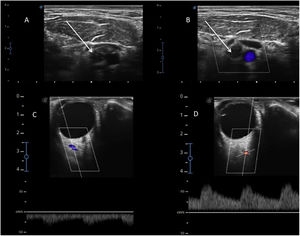
This is the case of a patient with complete occlusion of the internal carotid artery (Fig. 1A and B, arrows). A Doppler study using a transorbital approach of the ipsilateral ophthalmic artery reveals the presence of reversed Flow because the ophthalmic artery is being filled through naso-angular anastomosis where the external carotid artery meets the branches of the internal carotid artery via the facial artery nasal branch that anastomoses with the orbital branch of the ophthalmic artery (Fig. 1C). The Doppler ultrasound of the contralateral ophthalmic artery (Fig. 1D) reveals a positive flow for comparison purposes. Flow reversal in the ophthalmic artery is a specific ultrasound sign of critical or complete occlusion of the ipsilateral internal carotid artery.
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more