This study explored the link between the TG/HDL ratio and mortality in obese sepsis patients using the eICU database.
DesignRetrospective observational study.
SettingIntensive Care Medicine.
PatientsAccording to Sepsis 3.0 criteria, sepsis is diagnosed with infection and a SOFA score ≥2. This study included adults (age ≥18) with ICU stays ≥48 h to ensure data stability. Patients with diabetes, acute pancreatitis, or those on lipid-lowering or antidiabetic treatments were excluded due to their impact on lipid and glucose metabolism, which could bias the analysis of the TG/HDL ratio and all-cause mortality.
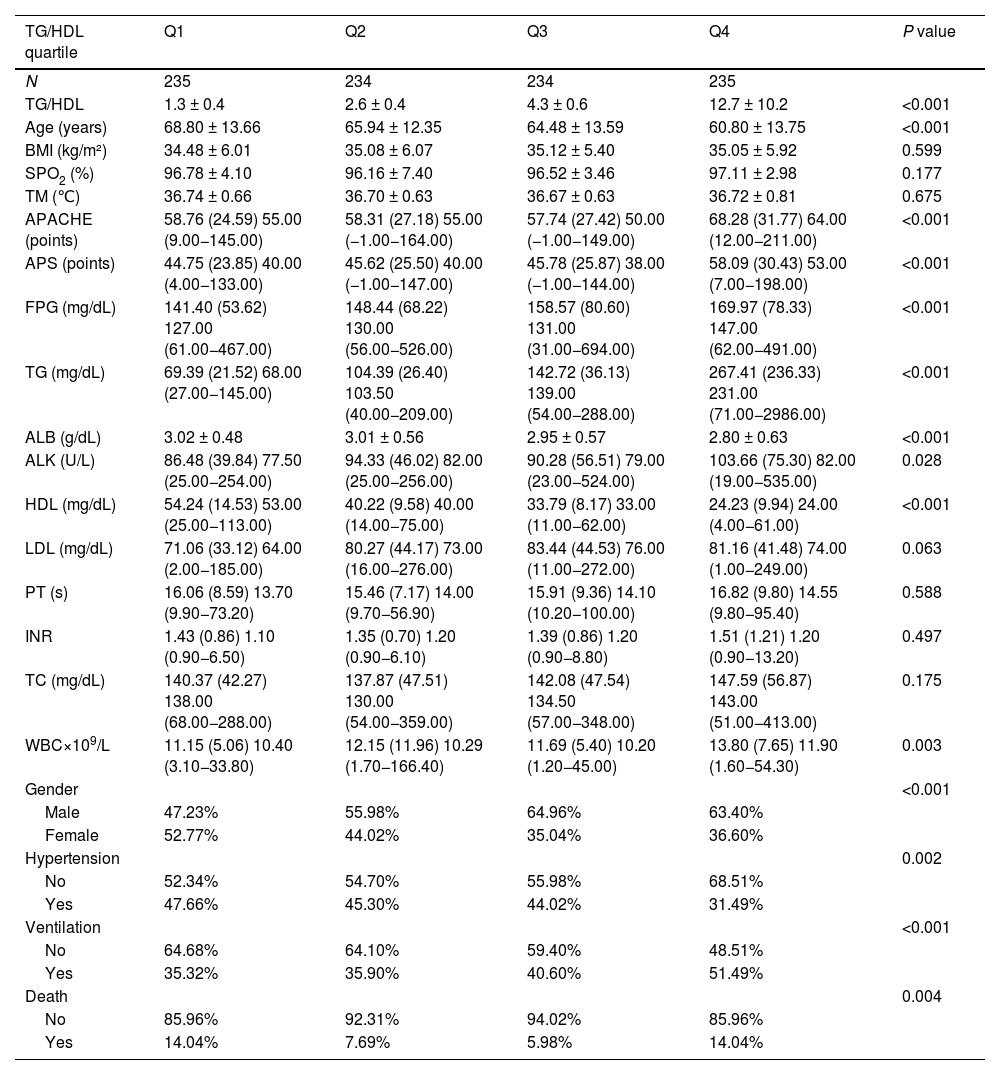
Interventions938 obese sepsis patients were selected, and statistical methods (variable assessment, difference test, regression model, curve fitting, subgroup analysis) were used. The study was carried out using R 4.3.2 software.
Main variables of interestTG/HDL.
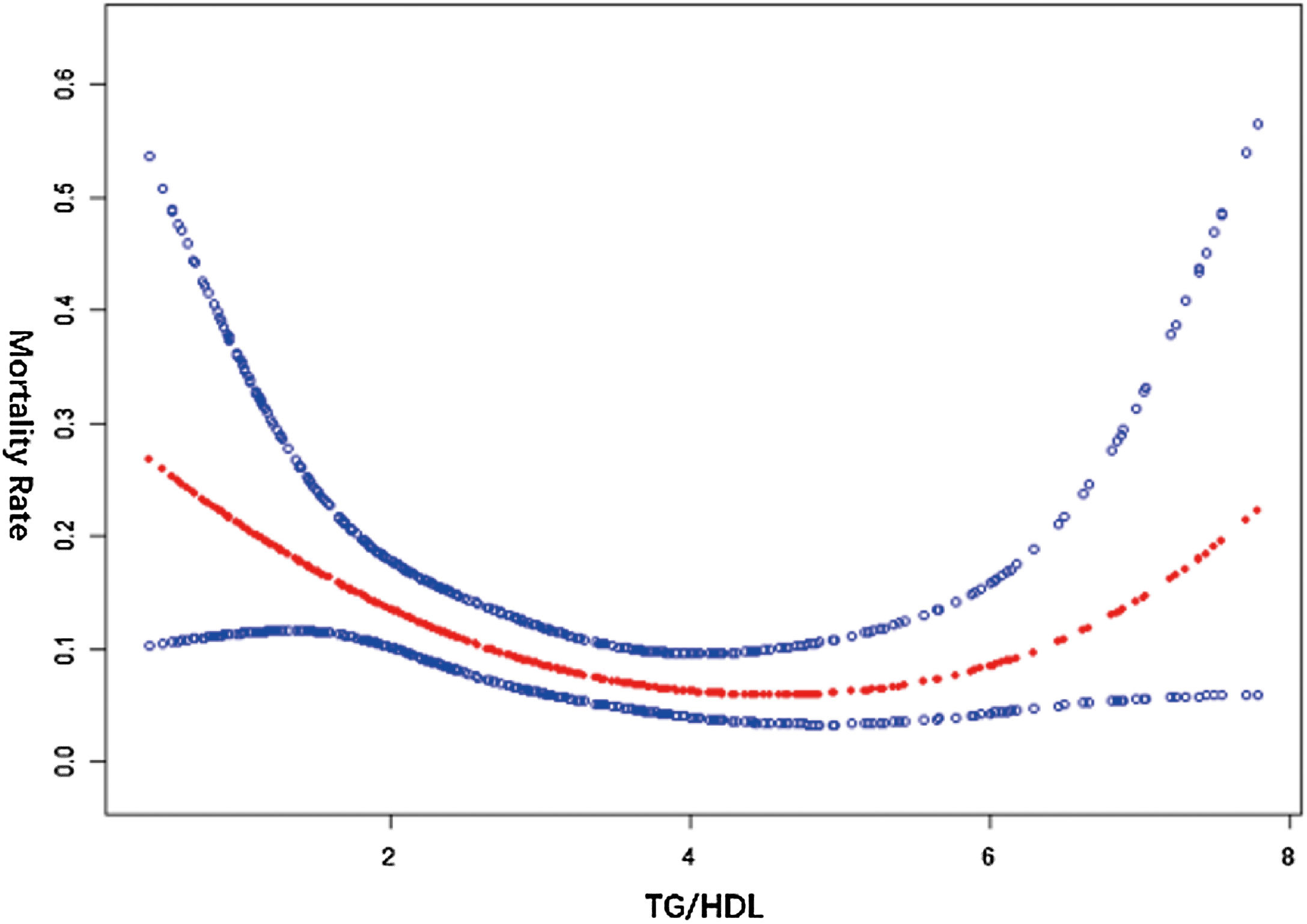
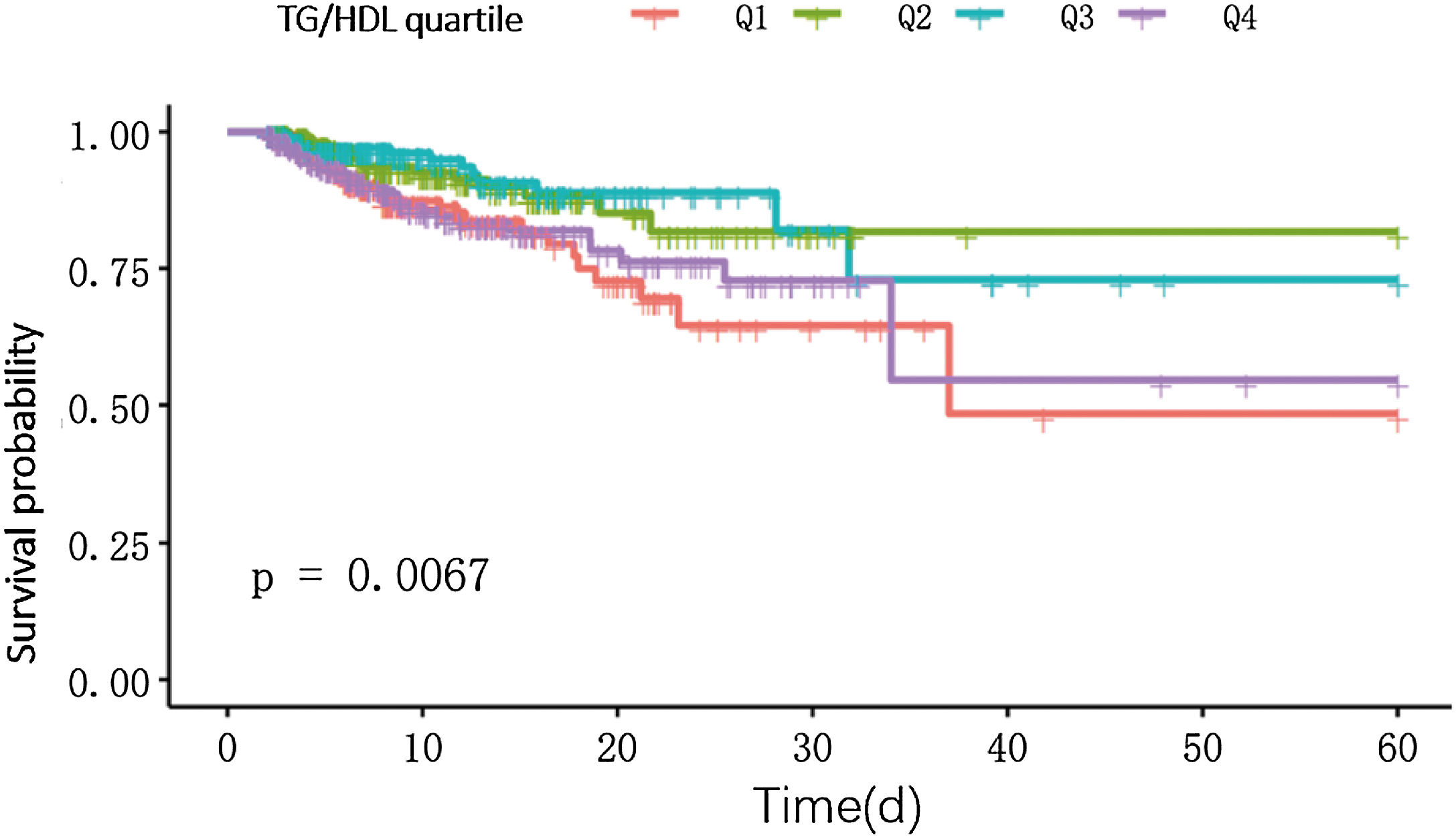
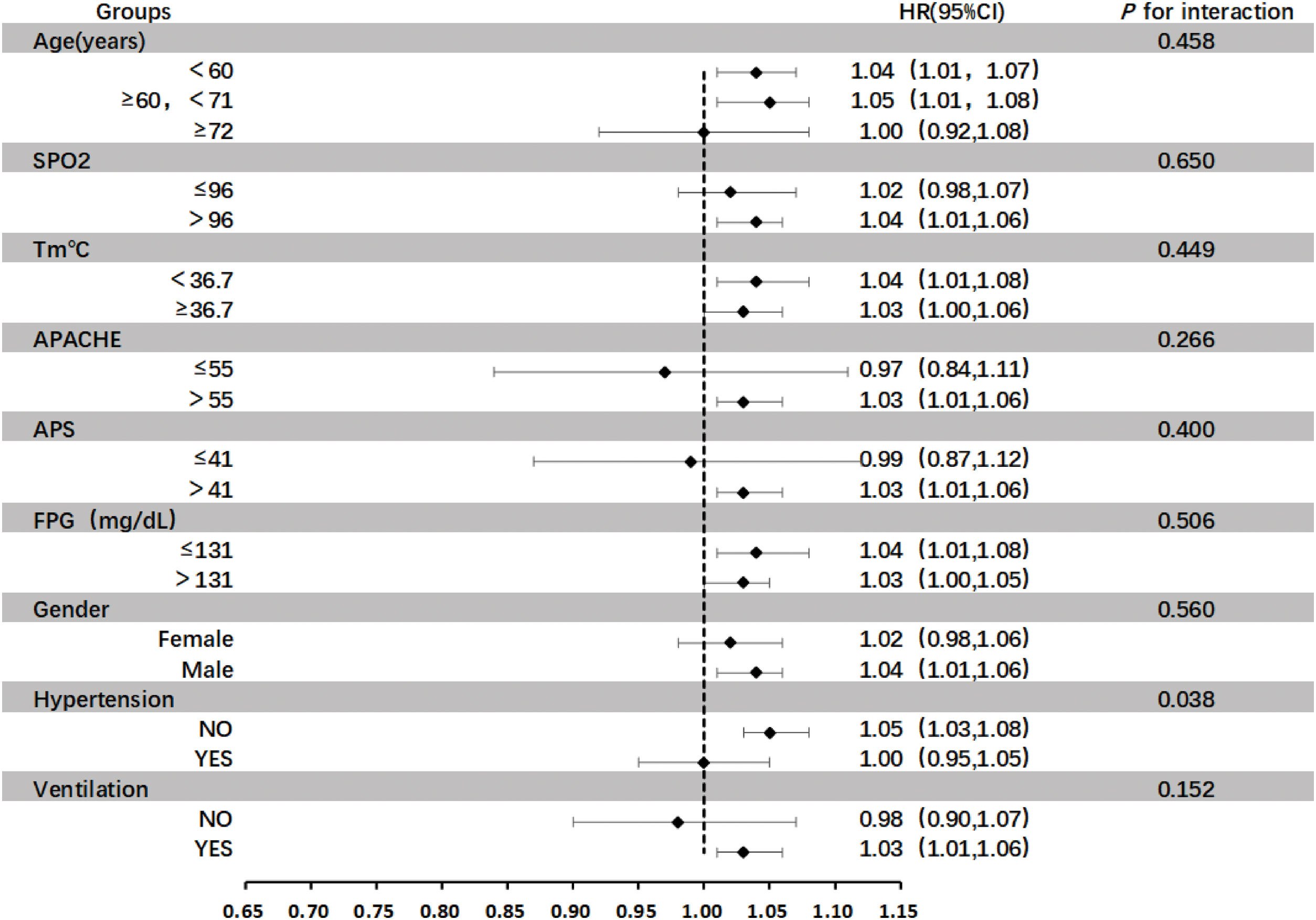
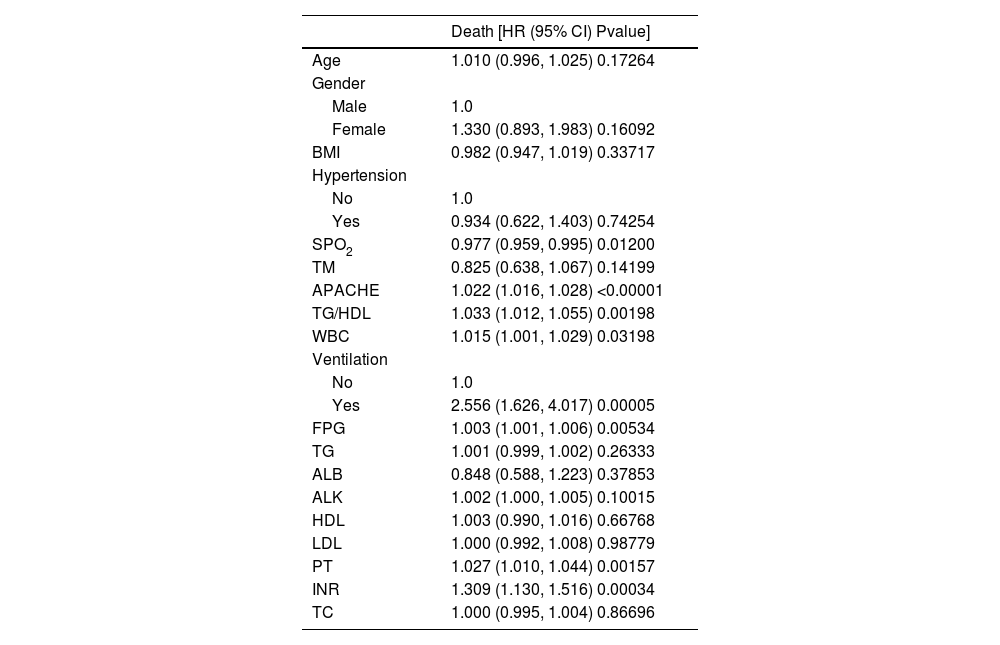
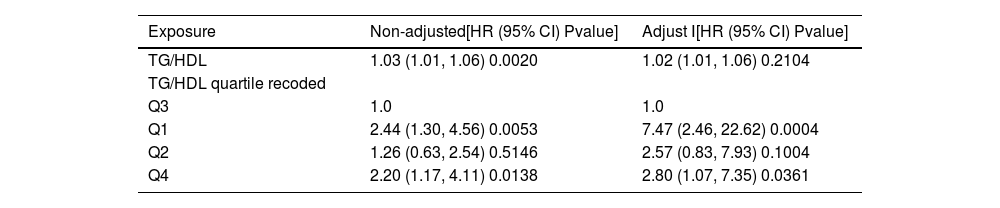
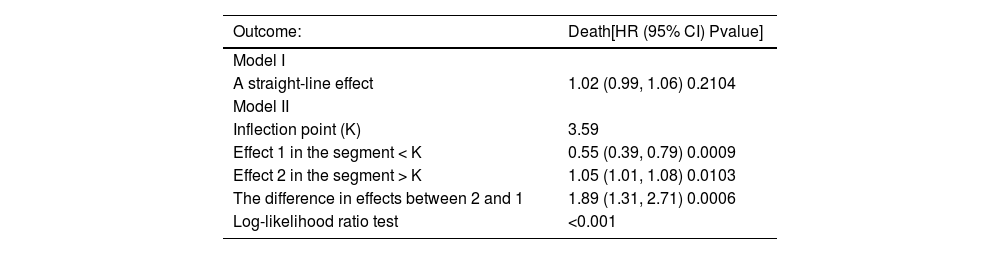
ResultsThe TG/HDL ratio varied across quartiles and was significantly linked to mortality in obese sepsis patients. Regression and curve fitting showed a U-shaped relationship for TG/HDL < 8, with an inflection point at 3.59. The K–M curve confirmed this U-shaped pattern, and subgroup analysis revealed a significant interaction with hypertension.
ConclusionsA U-shaped relationship exists between TG/HDL and mortality in obese sepsis patients, with both low and high levels increasing death risk.
Este estudio exploró la relación entre la razón TG/HDL y la mortalidad en pacientes obesos con sepsis utilizando la base de datos eICU.
DiseñoEstudio observacional retrospectivo.
ÁmbitoMedicina de Cuidados Intensivos.
PacientesSegún Sepsis 3.0, la sepsis se diagnostica con infección y SOFA ≥ 2. Se incluyeron adultos en UCI ≥ 48 horas, excluyendo a pacientes con diabetes, pancreatitis aguda o tratamientos que afecten lípidos y glucosa para evitar sesgos.
IntervencionesSe seleccionaron 938 pacientes obesos con sepsis, y se utilizaron métodos estadísticos (evaluación de variables, prueba de diferencias, modelo de regresión, ajuste de curvas, análisis de subgrupos). El estudio se realizó utilizando el software R 4.3.2.
Variables de interés principalesTG/HDL.
ResultadosLa razón TG/HDL varió entre cuartiles y se asoció significativamente con la mortalidad en pacientes obesos con sepsis. El análisis mostró una relación en forma de U para TG/HDL < 8, con un punto de inflexión en 3.59. La curva K-M y el análisis de subgrupos confirmaron este patrón, destacando una interacción con la hipertensión.
ConclusionesExiste una relación en forma de U entre el TG/HDL y la mortalidad en pacientes obesos con sepsis, siendo los niveles tanto bajos como altos los que aumentan el riesgo de muerte.
Article
Go to the members area of the website of the SEMICYUC (www.semicyuc.org )and click the link to the magazine.