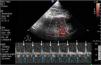
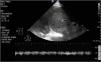
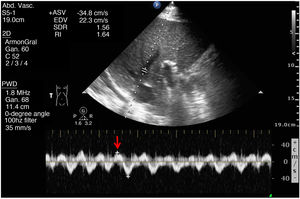
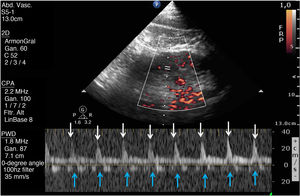
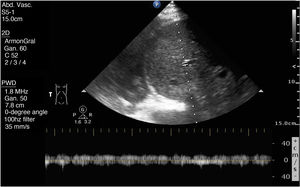
This is the case of an 86-year-old man admitted to the ICU due to right-sided heart failure (RSHF) after Mitraclip® implantation, severe chronic pulmonary hypertension, acute kidney injury, and elevated levels of transaminase and bilirubin. The VExUS (Venous Excess Ultrasound Score) system was used. Fig. 1 shows flow reversal during ventricular systole on the Doppler echocardiography of suprahepatic veins (red arrows). Fig. 2 shows the monophasic renal interlobar venous Doppler flow pattern (lack of venous flow [blue arrows] in systole [white arrows]). Both findings are suggestive of severe systemic venous congestion (SVC). However, portal vein Doppler (PVD) (Fig. 3) was not pulsatile (as it would have been expected in SVC). Cirrhosis-induced portal fibrosis (due to RSHF) prevents the transmission of pulsatility across venous flow being PVD, in this case, not assessable with the VExUS to diagnose SVC due to being a false negative outcome.
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more