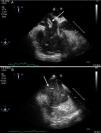
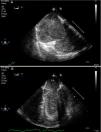
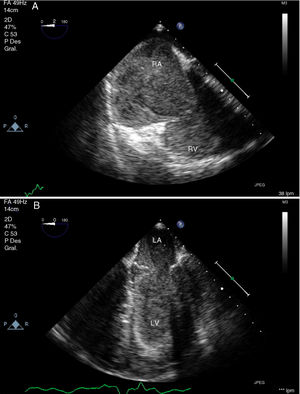
A 44-year-old man was admitted to our ICU due to thoracic trauma with associated bilateral pulmonary contusion. He developed severe refractory respiratory failure (PaO2/FiO2<100) and hemodynamic instability secondary to hypoxemia. Due to the inability to oxygenate the patient, it was decided to begin with veno-venous ECMO therapy. During cannulation of the femoral vein, a large thrombus (white arrow) was observed in the right atrium passing through the tricuspid valve into the pulmonary artery (Fig. 1); suddenly, the patient suffered cardiac arrest in pulseless electrical activity (Fig. 2), requiring advanced CPR maneuvers, recovering spontaneous circulation once ECMO therapy begun (Video). He remained under ECMO for seven days, after which, it was withdrawn due to respiratory improvement. He presented full neurological recovery.
El factor de impacto mide la media del número de citaciones recibidas en un año por trabajos publicados en la publicación durante los dos años anteriores.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación.
Ver másSNIP permite comparar el impacto de revistas de diferentes campos temáticos, corrigiendo las diferencias en la probabilidad de ser citado que existe entre revistas de distintas materias.
Ver más