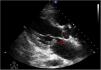
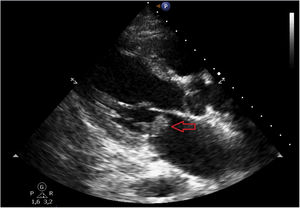
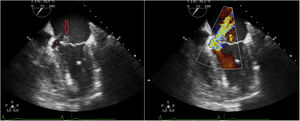
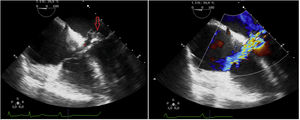
An 82-year-old hypertensive male with chronic renal failure subjected to hemodialysis, and with poor basal health, reported due to worsening of his general condition over the last two weeks. Complete atrioventricular block was diagnosed. The patient was admitted to the Intensive Care Unit under hemodynamically stable conditions and with conventional oxygen therapy. Transthoracic echocardiography revealed moderate mitral valve insufficiency and an image suggesting an anterior mitral leaflet vegetation (Fig. 1). Blood cultures proved positive for Staphylococcus aureus. Transesophageal echocardiography confirmed the presence of a 14 × 10 mm anterior mitral leaflet vegetation (A3) with evidence of a pseudoaneurysm (Fig. 2, *) at the base of the interatrial septum, and multiple fistulizations communicating the left ventricle outflow tract with both atria (Fig. 3). Surgical management was discarded in view of the poor basal condition of the patient.
Videos of the echocardiographic study have been included as Supplementary material, illustrating the description provided in the text.
FundingThis article has received no funding.
Conflicts of interestNo conflicts of interest.