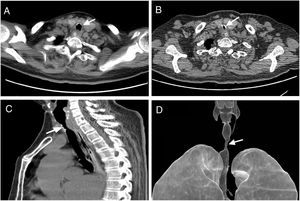
A 64-year-old woman with subarachnoid hemorrhage presented to intensive care unit. Endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation therapy were required for 11 days due to slowly recovery of consciousness and poor muscle strength. The cuff pressures and endotracheal tube positions were routinely checked. 11 days later, her trachea was extubated. However, 5 days after the removal of the tracheal catheter, the patient began to have mild dyspnea. Chest CT examination indicated slight tracheal stenosis (Fig. 1A, arrow). 23 days after extubation, the patient presented obvious inspiratory dyspnea, and tracheal CT indicated obvious tracheal stenosis (Fig. 1B–D, arrow). The patient was transferred to ICU, and the dyspnea was relieved after tracheal intubation again. To maintain the airway, elective tracheotomy was performed.
El factor de impacto mide la media del número de citaciones recibidas en un año por trabajos publicados en la publicación durante los dos años anteriores.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación.
Ver másSNIP permite comparar el impacto de revistas de diferentes campos temáticos, corrigiendo las diferencias en la probabilidad de ser citado que existe entre revistas de distintas materias.
Ver más