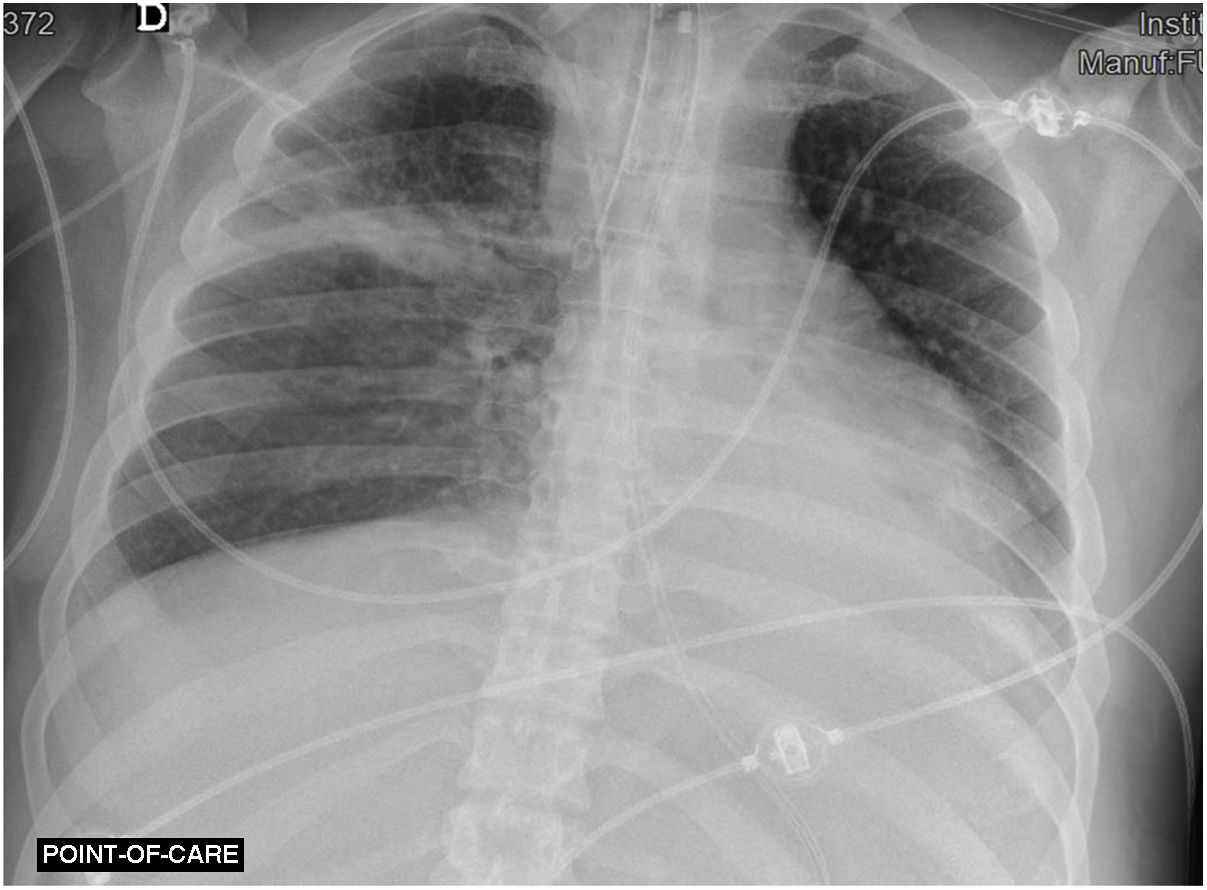
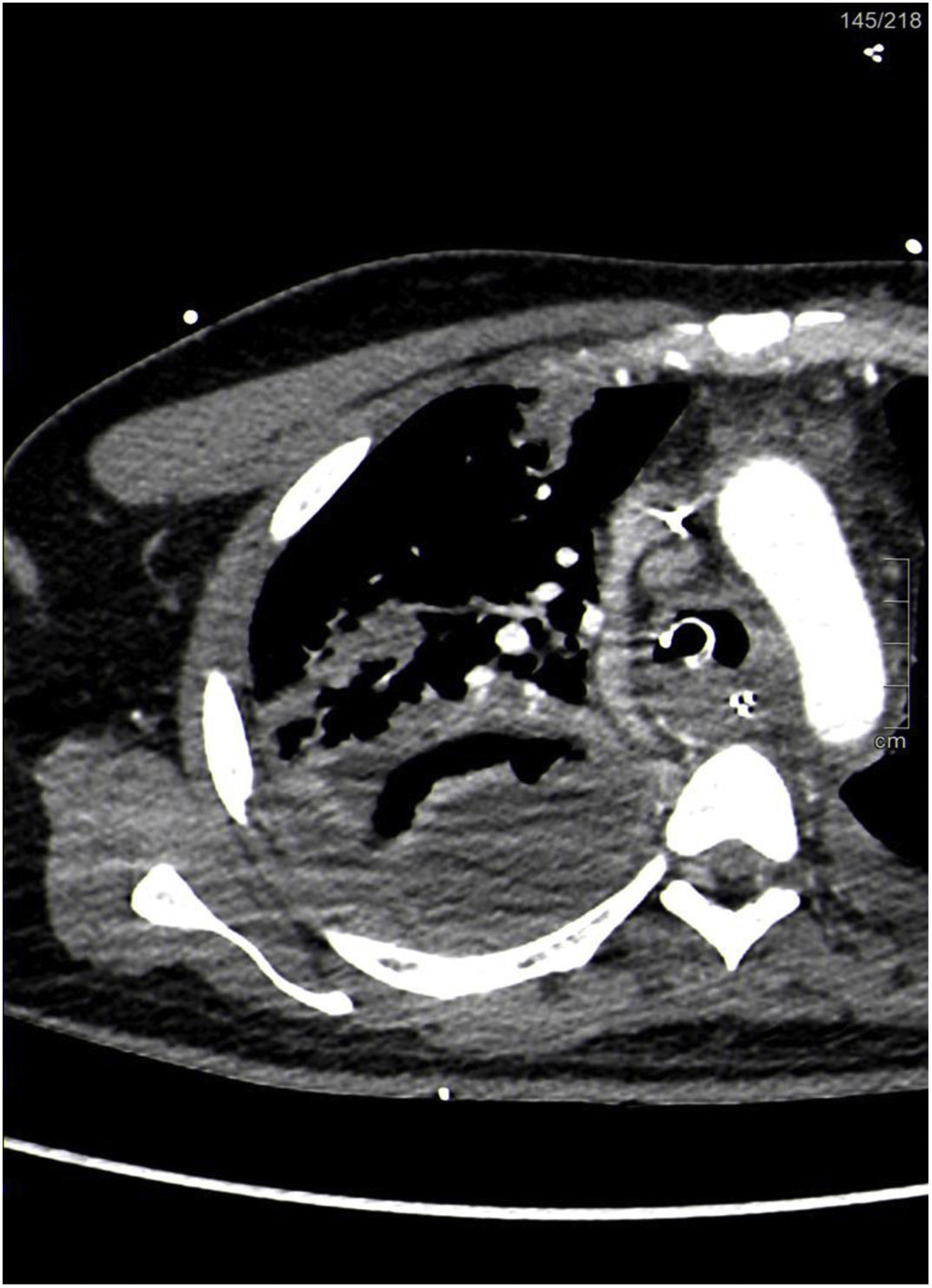
A 38-year-old man with no relevant medical history was hospitalized in the intensive care unit with fever and nonspecific respiratory symptoms, which rapidly progressed to severe respiratory failure, septic shock, and multiple organ failure. He required vasopressor support, invasive ventilation, and antibiotic treatment with penicillin, clindamycin, and linezolid after Streptococcus pyogenes was isolated in respiratory samples and blood cultures. Despite treatment, fever persisted, as did a consolidation on the chest X-ray (Figure 1). Computed tomography (Figure 2) revealed necrosis and a lung abscess in the right upper lobe. This case highlights a severe presentation of invasive Streptococcus pyogenes infection, emphasizing the need to consider this etiology in the differential diagnosis, even in patients without known risk factors.
Declaration on the use of generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the drafting process: the authors used ChatGPT to enhance the language and readability during the preparation of this work. After using this tool, the authors reviewed and edited the content as necessary and assume full responsibility for the publication’s content.
FundingNone declared.
Conflicts of interestNone declared.
Please cite this article as: Abril-Victorino JM, Ruiz de la Cuesta-López M, Gómez-Camino S. Neumonía grave adquirida en la comunidad por Streptococcus pyogenes. Med Intensiva. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medin.2024.05.012