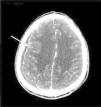
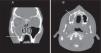
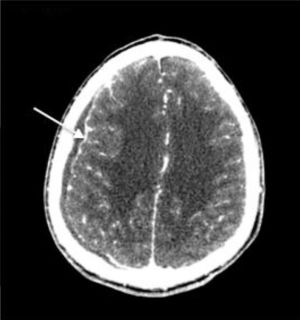
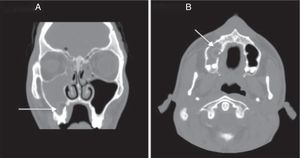
Twenty-one-year-old male patient with right-sided hemicrania continua headache, fever and purulent rhinorrhea presented with a diagnosis of right maxillary sinusitis that remains unresponsive to antibiotic therapy. The patient was re-evaluated more than 10 days after showing these symptoms, and one craniofacial TC scan with contrast was conducted that confirmed right pansinusal involvement and one extense extra-axial subdural frontoparietal ipsilateral collection that was consistent with empyema (Fig. 1). Urgent neurosurgery was performed with evacuation of the subdural suppurated collection. After reviewing the CT scan, one round unilocular lesion was seen with well-established edges inside the right maxillary sinus and associated with piece 16 and consistent with a complex periapical cyst (Fig. 2A and B). After identifying the primary focus of infection, one exodontia procedure was performed resulting in abundant pus and curettage of the sinus with favorable clinical progression.
Please cite this article as: Palomo López N, Freire Aragón MD, Rivera Fernández V. Empiema subdural secundario a sinusitis maxilar de origen odontógeno. Med Intens. 2018;42:e21–e22.