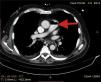
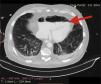
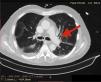
A 72-year-old man, previously independent, was admitted to the emergency department following cardiorespiratory arrest. A chest computed tomography scan (CTS) was requested. During the exam, the patient experienced sudden hypotension (65/20&#¿;mmHg) and poor peripheral perfusion. The exam was suspended and a fluid bolus was administered, resulting in transient reversal of the condition. Gas was detected in the injection system, which was replaced, and the exam was repeated. The CTS revealed gas embolism with an air-fluid level in the main pulmonary artery (marked with an arrow in Fig. 1), right atrium and right ventricle (marked with an arrow in Fig. 2), as well as in the left upper lobar artery (marked with an arrow in Fig. 3). Due to the venous gas embolism, he was transferred for treatment at a hyperbaric medicine center.
El factor de impacto mide la media del número de citaciones recibidas en un año por trabajos publicados en la publicación durante los dos años anteriores.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación.
Ver másSNIP permite comparar el impacto de revistas de diferentes campos temáticos, corrigiendo las diferencias en la probabilidad de ser citado que existe entre revistas de distintas materias.
Ver más