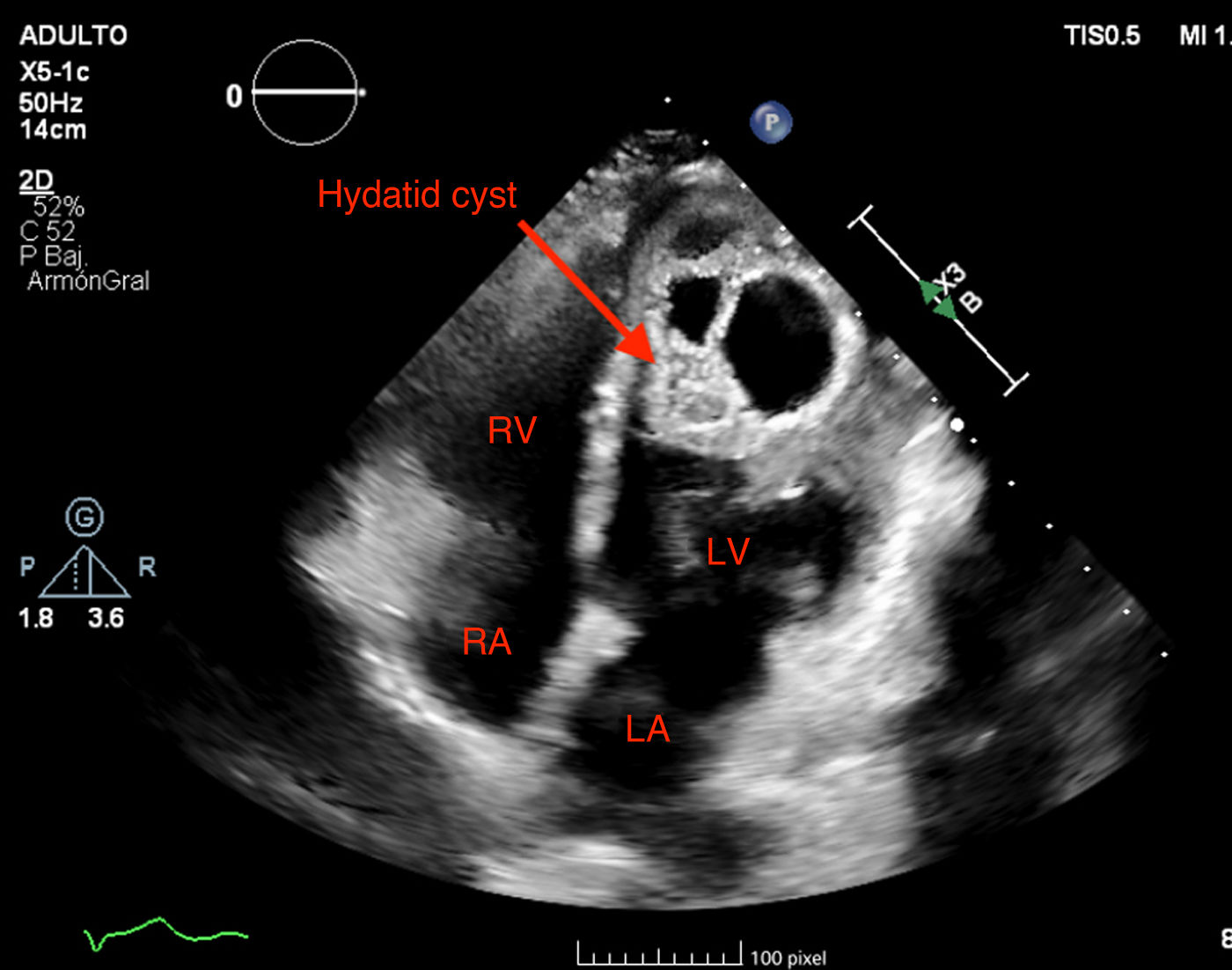
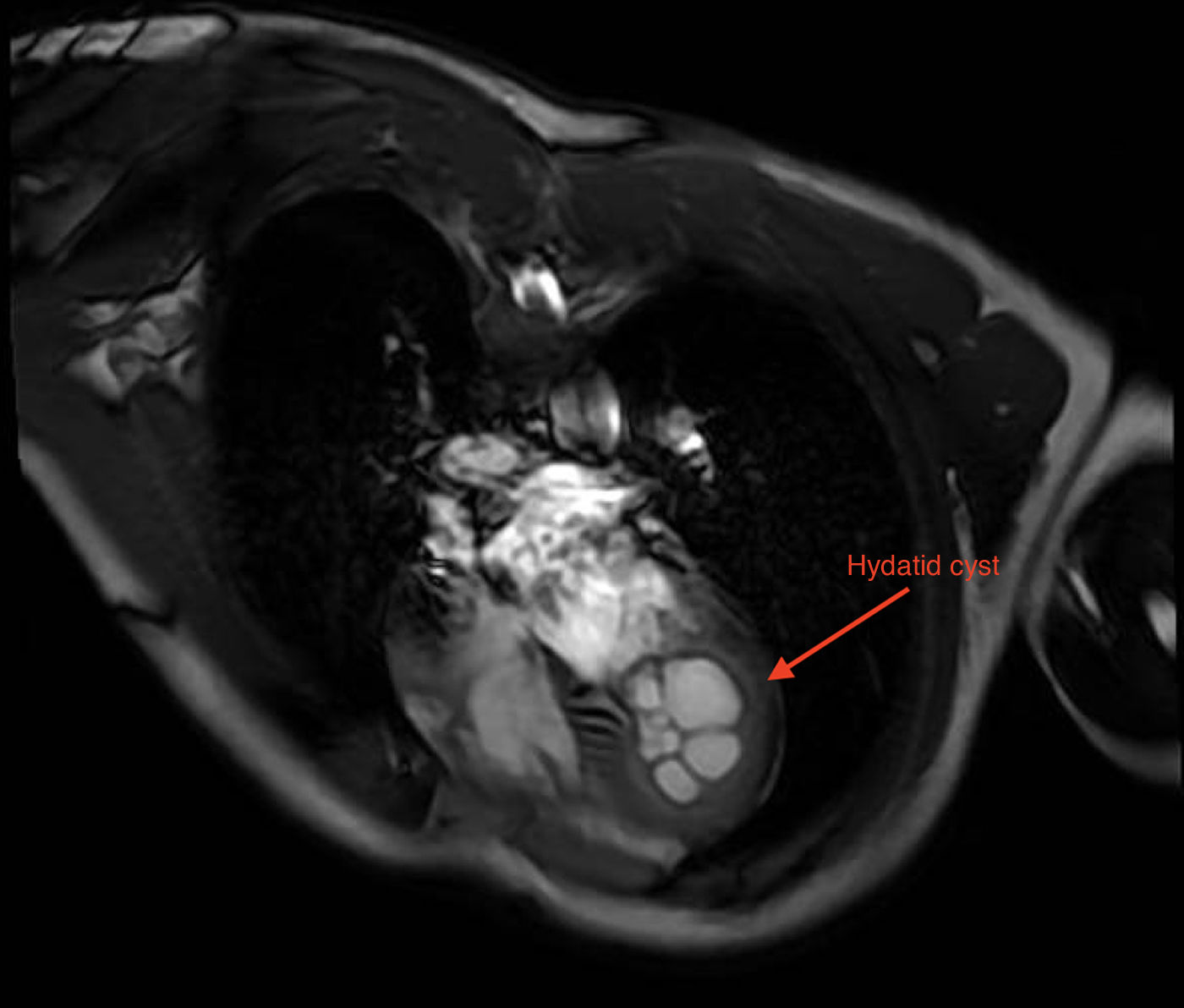
Hydatidosis is an infection caused by Echinococcus granulosus. Dogs act as the primary reservoir and sheep as intermediate hosts. Humans are accidentally infected by consuming food contaminated with dog feces. The main sites of infection are the liver or lungs; cardiac hydatidosis (CH) is very rare (0.5%–2%).
This is the case of a 33-year-old man from Morocco who sought consultation with a 3-month history of dyspnea and chest discomfort. An ultrasound (Fig. 1) identified the presence of a cystic mass in the apex of the left ventricle. Diagnosis was completed with an MRI, which characterized the cyst as hyperintense on T2-weighted images (Fig. 2). Symptoms of cardiac hydatidosis depend on the degree of pericardial and coronary compression, and the mass itself. Transthoracic ultrasound offers good sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis, which was confirmed by pathological anatomy during the intervention, which involved resection of vesicles with protection of the surgical bed using hypertonic scolicidal saline. Upon discharge, the patient remained on albendazole treatment for, at least, 6 months.
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing processNo AI technology was used in the preparation of this article, manuscript, or images.
FundingNone declared.
None declared.