The present study highlights the advances in ultrasound, especially regarding its clinical applications to critically ill patients.
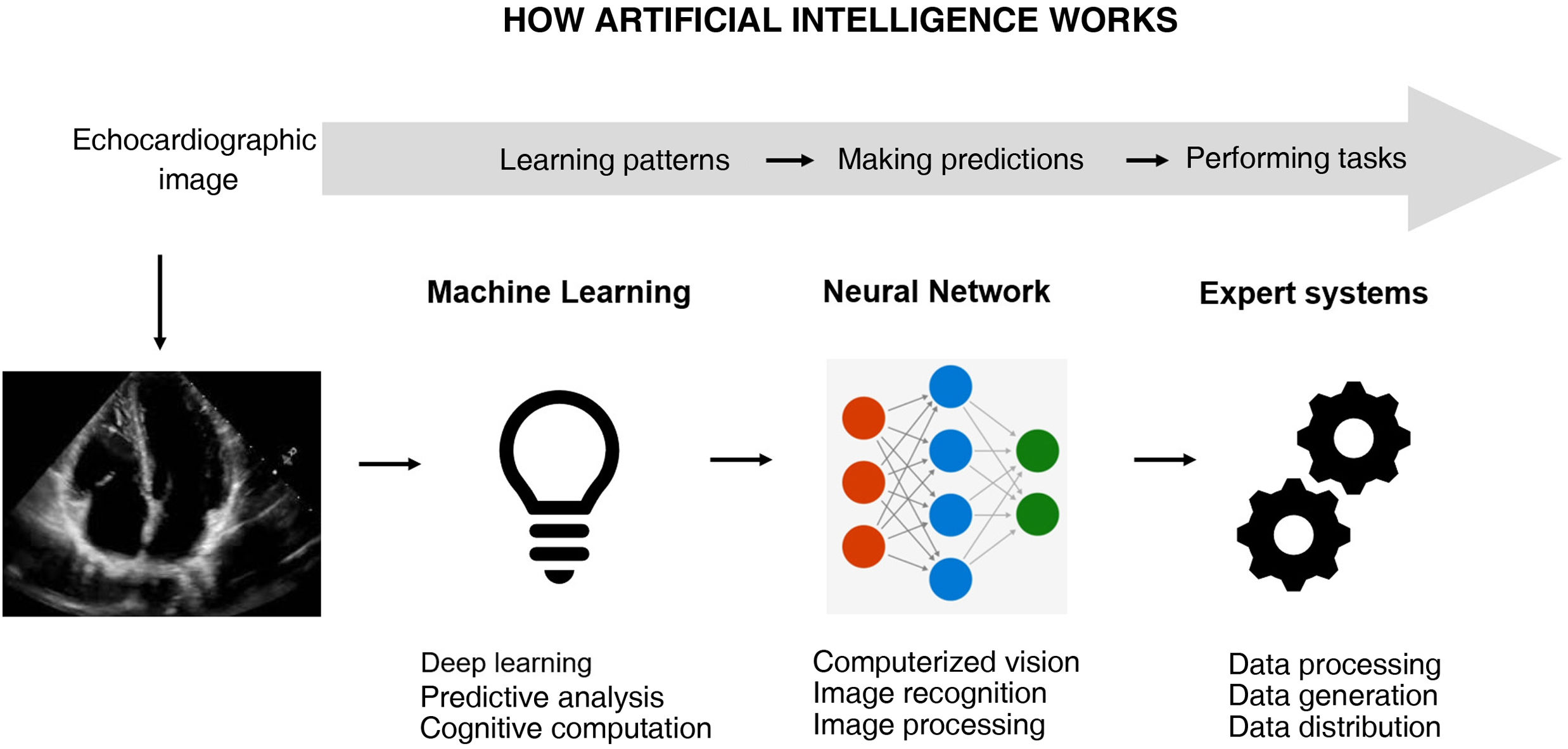
Artificial intelligence (AI) is crucial in automating image interpretation, improving accuracy and efficiency. Software has been developed to make it easier to perform accurate bedside ultrasound examinations, even by professionals lacking prior experience, with automatic image optimization. In addition, some applications identify cardiac structures, perform planimetry of the Doppler wave, and measure the size of vessels, which is especially useful in hemodynamic monitoring and continuous recording. The "strain" and "strain rate" parameters evaluate ventricular function, while "auto strain" automates its calculation from bedside images. These advances, and the automatic determination of ventricular volume, make ultrasound monitoring more precise and faster. The next step is continuous monitoring using gel devices attached to the skin.
El artículo destaca los avances en ecografía, especialmente en su aplicación clínica para pacientes críticos.
La inteligencia artificial (IA) juega un papel crucial al automatizar la interpretación de imágenes, mejorando la precisión y eficiencia. Se han desarrollado softwares que facilitan la realización de exámenes ecográficos precisos a pie de cama, incluso para personal sin experiencia previa, con la optimización de la imagen de manera automática. Además, existen aplicaciones que identifican estructuras cardíacas, planimetran la onda Doppler y miden el tamaño de vasos, que son especialmente útiles en la monitorización hemodinámica y en su registro continuo. Los parámetros "strain" y "strain rate" evalúan la función ventricular, mientras que el "auto strain" automatiza su cálculo desde imágenes a pie de cama. Estos avances, junto con la determinación automática del volumen ventricular hace que la monitorización con ultrasonidos sea más precisa y rápida. El siguiente paso es la monitorización continua por dispositivos geles adheridos a la piel.
The present article examines the main advances in echocardiography, focusing especially on their clinical applications. We often find that technological advances and improvements in ultrasound, generally in the context of imaging analyses, do not translate effectively into care for the critically ill. We therefore will concentrate on those developments that really contribute to add value in our specialty and at the patient bedside, discarding those advances that require an offline analysis.
Echocardiography has important limitations that influence its use and precision, such as optimum image acquisition, inter-operator variability, its use as a hemodynamic monitoring tool, and the precise measurement of heart function and structure.1,2 These aspects are crucial for the applicability and reliability of the technique in clinical practice, and it is in these areas that we will comment on the advances that may help us most.3–5
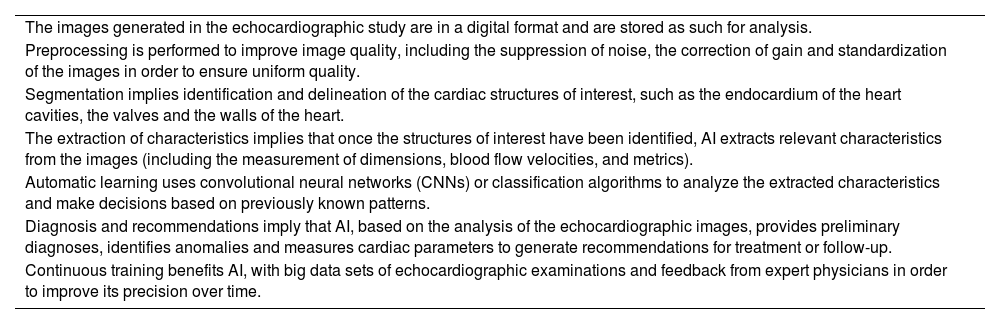
Artificial intelligence (AI) is undoubtedly of fundamental help6,7 (Fig. 1). The automation of images saves time and resources, but deep learning algorithms such as convolutional networks and transformers have moreover shown a strong potential for extraction of the most important characteristics of images and their interpretation.8,9 The processing of medical images includes the suppression of background noise and the adjustment of brightness and contrast, homogenizing size and standardizing pixel intensities. Interpretation based on AI is somewhat more complex and requires problem adjustment – whether the classification of the images, their segmentation, or the detection of objects in them – in order to focus on the relevant aspects subject to analysis10,11 (Table 1).
Artificial intelligence (AI) can use unprocessed echocardiographic images/videos to automatically provide structural or functional parameters, but it can also identify pathological conditions. Image processing arises from deep analyses based on the pixel, performed repeatedly. This also implies analysis and improvement of image quality in order to extract information.
Technical aspects of image processing and automatic learning with artificial intelligence (AI).
| The images generated in the echocardiographic study are in a digital format and are stored as such for analysis. |
| Preprocessing is performed to improve image quality, including the suppression of noise, the correction of gain and standardization of the images in order to ensure uniform quality. |
| Segmentation implies identification and delineation of the cardiac structures of interest, such as the endocardium of the heart cavities, the valves and the walls of the heart. |
| The extraction of characteristics implies that once the structures of interest have been identified, AI extracts relevant characteristics from the images (including the measurement of dimensions, blood flow velocities, and metrics). |
| Automatic learning uses convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or classification algorithms to analyze the extracted characteristics and make decisions based on previously known patterns. |
| Diagnosis and recommendations imply that AI, based on the analysis of the echocardiographic images, provides preliminary diagnoses, identifies anomalies and measures cardiac parameters to generate recommendations for treatment or follow-up. |
| Continuous training benefits AI, with big data sets of echocardiographic examinations and feedback from expert physicians in order to improve its precision over time. |
We will focus not on the how but on the evolution itself, which has led to a revolution in ultrasound applied to the critically ill.
Cardiac image acquisition and recognitionThe acquisition of optimum and reproducible echocardiographic images in intensive care is challenging. Not only the positioning of the patient but also the limited cooperation involved, the interpositioning of surgical dressings, and assisted ventilation imply that obtaining an optimum window over several cardiac cycles in which to perform measurements is not feasible in some cases – a fact that limits the precision and diagnostic performance of the technique.
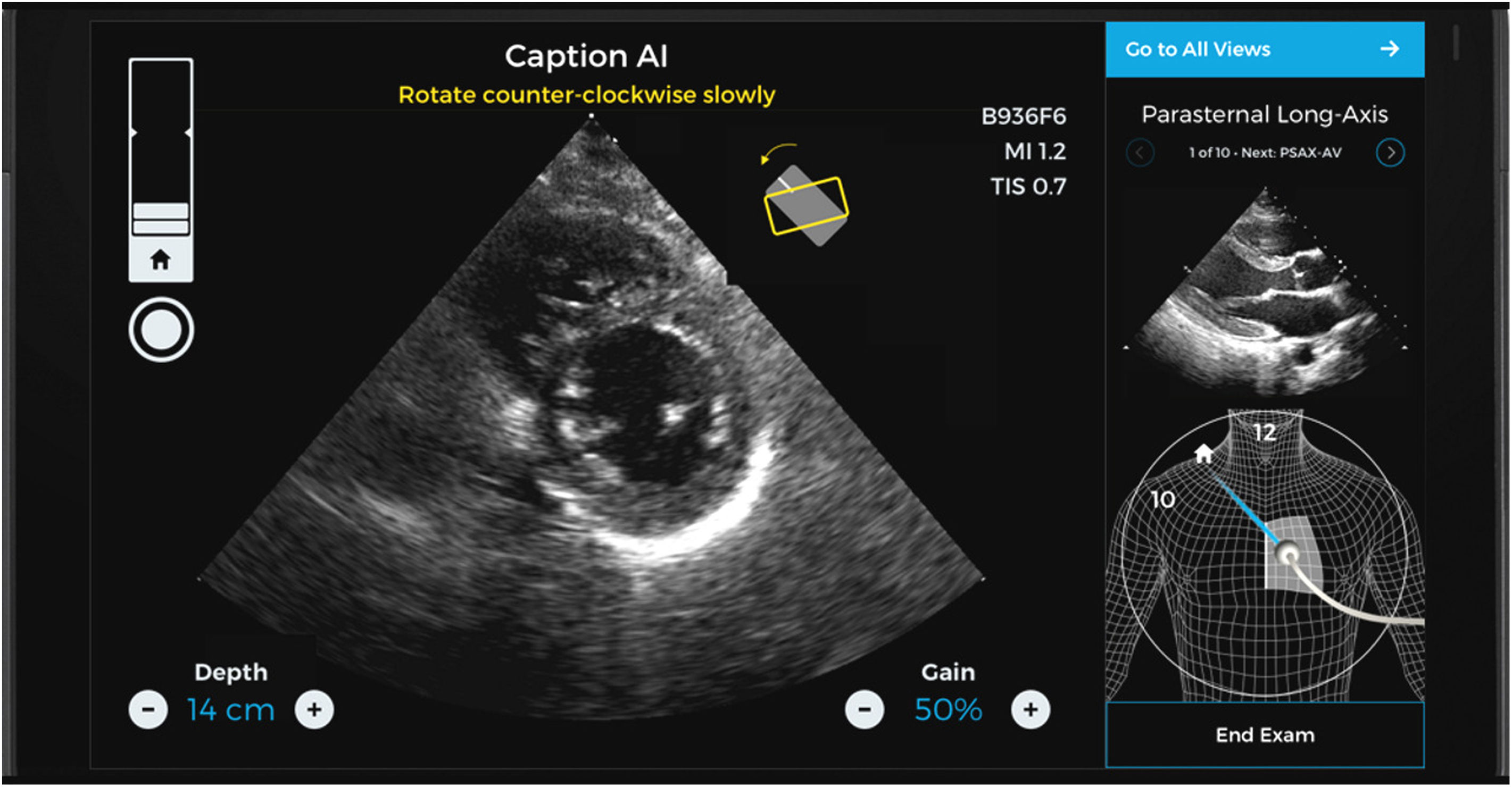
Caption AI© and Caption Guidance© are new software applications allowing intensivists – even those with no prior experience in ultrasound – to perform echocardiographic explorations quickly, precisely and at the patients bedside.12–14 This novel software combines immediate information on the orientation and inclination of the transducer in order to optimize the image and at the same time automatically assess its quality – increasing the capacity to secure an intelligent interpretation of the exploration (Figs. 2 and 3).15,16
Two-plane views of a study made with the help and guidance of Caption AI© and Caption Guidance©. Different aid items are available that guide the transducer until an optimum plane is recognized and obtained (including even classification of the degree of optimization achieved). The best loop is automatically recorded, and the measures that can be obtained from it are displayed.
Caption AI© recognizes the structures through artificial intelligence, and Caption Guidance© affords the precise orientation of the transducer at the patient bedside during the exploration. Both applications generate real-time feedback on imaging quality in order to secure automatic high-quality image capture.17–19 This technology allows continuous monitoring of the best images seen during each scan, automatically capturing the image of greatest precision from each window. Automatic review of the clips obtained classifies them according to image quality, selecting the best ones for calculating basic exploratory parameters. The operator can explore each plane with the confidence of always being able to access the best two-second clip for examination by simply pressing a button (Video 1, Supplementary material).20
Their reliability has been certified by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and in this regard the studies cited above have analyzed over four million images corresponding to examinations performed by inexperienced physicians, in which calculation of the ejection fraction (EF) and its algorithm were found to be precise and reliable even in obese patients with impaired or normal cardiac function.
Clinical application in critically ill patients:
- -
Optimization of ultrasound images
- -
Reduction of intra- and inter-operator variability
- -
Automatic saving of images
Image identification and recognition is not the only important consideration in critically ill patients. These subjects accumulate tests and studies, and it is important to be able to file these data for successive and continuous analysis. This is a key aspect, since immediate information is constantly contrasted against previously obtained information in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). The facilitation of repeated and grouped data consultation corresponding to the same patient is therefore of great help in analyzing his or her evolution over time.
Different commercial software applications are available for automatically identifying cardiac, vascular and pulmonary structures, as well as for delimiting Doppler waves, from a hemodynamic perspective closely oriented toward the critically ill patient.21,22
- -
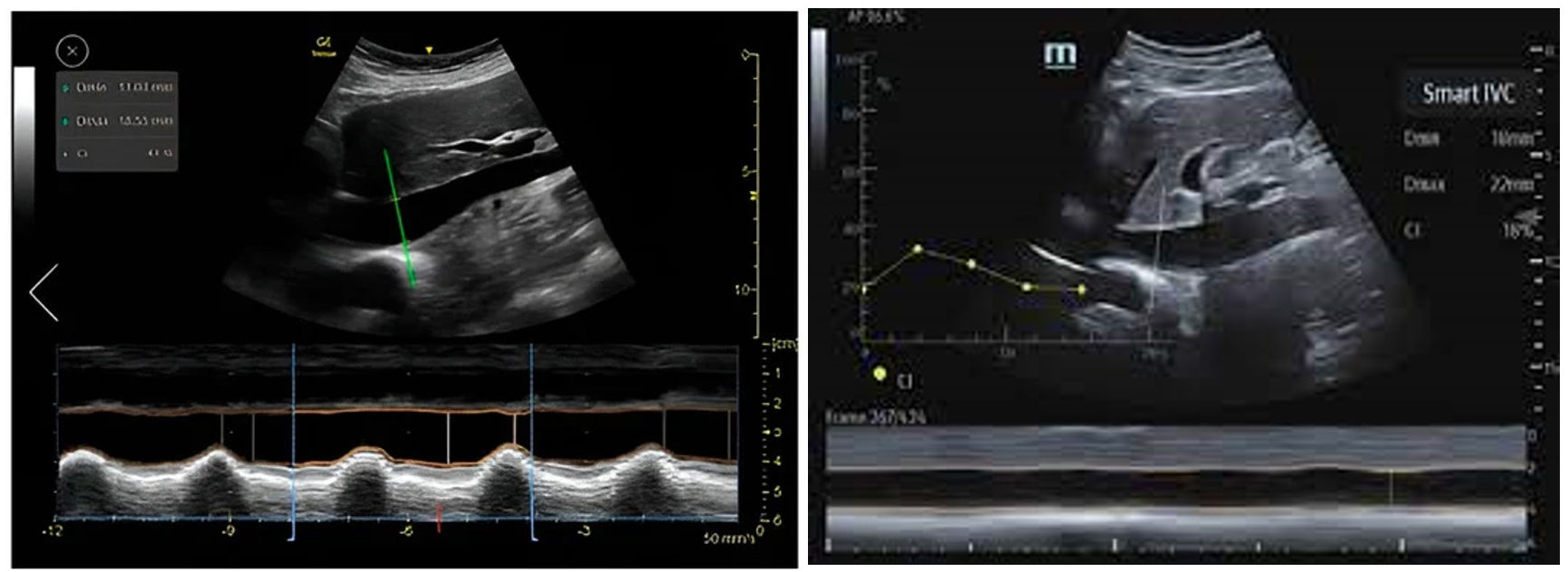
Automatic assessment of the inferior vena cava (IVC) as a surrogate marker of preload and response to volume replacement allows optimum and precise evaluation of the vein with regard to its major diameters, and measurement of its collapsibility or distensibility (Fig. 4).23 Reliability is equivalent to the capacity of an expert in 87% of the cases.24–27
Figure 4.Automatic definition of the margins of the inferior vena cava (IVC) using Venue GE© and Smart Fluid Mindray© from the subcostal plane, with continuous monitoring: the green color contour does not appear until the plane is optimized, and on freezing the image, automatic calculations are made of the maximum and minimum diameters in order to apply the IVC collapsibility formula.
- -
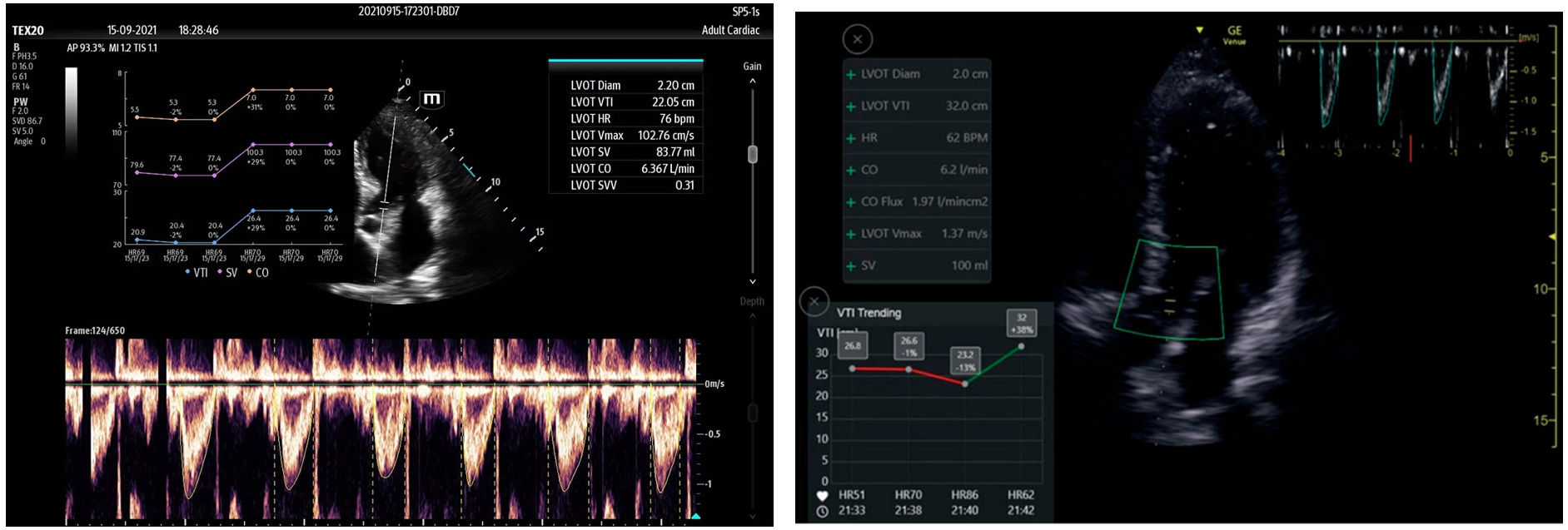
Automatic assessment of the velocity-time integral (VTI) in the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), as a surrogate marker of cardiac output, and its variability in the context of mechanical ventilation, is used to predict response to volume replacement. It identifies the largest and best-defined pulsed Doppler wave contour, and its variation with patient respiration. The recording can be filed, generating a trend plot that is of help in quickly visualizing the time course, becoming a monitoring technique (Fig. 5).28 Reliability is equivalent to the capacity of an expert in 82% of the cases.29–31
Figure 5.Automatic detection of the velocity-time integral (VTI) in the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) using Venue GE© and Smart Fluid Mindray©. Automatic detection and planimetry of the pulsed Doppler wave when its tracing is clearest and the area is greatest, analyzing its variability over several respiratory cycles. The trend is recorded, with the values corresponding to systolic volume and cardiac output during ad mission.
- -
Automatic assessment of the B lines in the lung fields, as a lung congestion surrogate allows the software to calculate the number, consistency and thickness of the B lines, storing this information according to the thoracic segments explored and the examinations made, in order to subsequently visualize the evolution over time in the serial form.32–34 The LungSweep© application allows a sweep in thoracic exploration according to the intercostal space and lung segment explored (Figure S1, Supplementary material).35 This recording generates a lung aeration map of use in diagnosing pneumonia. The exploration according to lung segments makes it possible to identify the number, thickness and consistency of the pulmonary B lines (Figure S2, Supplementary material).36 Reliability is equivalent to the capacity of an expert in 86% of the cases.37–39
Clinical application in critically ill patients:
- -
Assessment of preload, volemia and response to fluid replacement
- -
Assessment and trends in cardiac output
- -
Assessment of lung congestion
- -
Aggregation and analysis of ultrasound data (hemodynamic trends)
"Strain" and "strain rate" are two recent parameters that require offline edition in the imaging workstation. Nevertheless, software has now been incorporated making it possible for some systems to calculate them automatically at the patient's bedside (point of care). This information is important, as it affords greater reliability in assessing intrinsic ventricular systolic function, and can also be used to assess diastolic function with the analysis of the left atrial contraction.
“Strain” refers to ventricular muscle fiber deformation during systole. When the heart contracts, the muscle fibers shorten in certain directions and elongate in others. “Strain” is a quantitative measure of this deformation, and is expressed as a percentage. A negative “strain” value indicates shortening, while a positive value indicates elongation. In echocardiography, “strain” is recorded using advanced techniques such as “speckle tracking”, monitoring the movement of small points in the myocardium of the ventricles and left atrium, fundamentally. The “strain rate” (deformation rate) refers to the rate at which ventricle muscle fiber deformation occurs, and measures how “strain” varies per unit time. The “strain rate” is expressed as units of length per unit of time (e.g., 1/s), and provides additional information on cardiac contraction compared with static “stain” alone40–42 (Figure S3, Supplementary material).43
“Strain” can also be used in the left atrium. The deformation of this cavity is directly related to the diastolic function of the left ventricle. The normal “strain” values of the left atrium can vary, though as a reference, the typical left atrial “strain” values tend to range between −20% and −30%.44–47
“Auto-strain” is a software parameter allowing some systems to automatically calculate myocardial “strain” from images at the patient's bedside without the operator having to perform manual measurements. The device only needs an apical image optimized as far as possible, in the four-chamber, two-chamber and three-chamber views. This automated function has become more common with the incorporation of image processing technologies and workflow analysis in echocardiography48–51 (Video 2,52 Video 3,53 Video 4,54 Supplementary material).
The generation of "auto-strain" is a further step in the automation of certain variables in ultrasound. We have already seen that “strain” is a better and more reliable measure than the ejection fraction, which is affected by artifacts secondary to many variables such as preload, postload and the inherent characteristics of myocardial distensibility. This parameter is extremely useful for exploring the right ventricle, which proves very difficult and variable in critically ill patients subjected to mechanical ventilation. Such software automatically provides information that will increase precision and change the terms of the systolic assessment of both ventricles.
Clinical application in critically ill patients:
- -
Reliable assessment of ventricular function
- -
Assessment of diastolic function and intraventricular pressures
Ventricular area and volume can be evaluated in different ways. The most common approach is the biplanar method, based on the sum of two discs (the modified Simpson’s rule) obtained from two-dimensional (2D) echocardiographic images (areas). The analysis of areas allows us to determine volumes, with values that can be used to calculate the ejection fraction (EF), systolic (stroke) volume, filling or end-diastolic volume, and cardiac output (CO). The limitations of the biplanar method are multiple, such as a clear view of the endocardium, imaging in a perfect longitudinal plane, alignment of the apex, or poor visualization in the apical two- and four-chamber views for volume estimation.
“Three-dimensional (3D) automated volume” in echocardiography is a software tool that allows the echocardiographic system to automatically generate a 3D volume of the heart without the operator having to perform manual measurements.55–57 This function is an advanced feature that allows us to obtain a 3D representation of the heart that can be useful for a more detailed evaluation of cardiac function and anatomy (Figure S4, Supplementary material)58 (Video 5 59, Supplementary material).
Due to its morphology, the most relevant clinical challenge in this regard is the right ventricle (RV). The determination of its end-diastolic volume is simply not possible with the disc system, which assumes a regular morphology to calculate volume from the areas, as in the case of the left ventricle (LV). The determination of RV volume can be very useful in the critically ill patient since it is known to adapt and change in response to increases in pressure or volume; its continuous monitoring in a patient under mechanical ventilation in the ICU, therefore, may be very relevant and can help improve ventilation management.60–62 (Figure S5 Supplementary material) 63 (Video 6,64 Supplementary material).
Clinical application in critically ill patients:
- -
Assessment of preload (LV end-diastolic volume)
- -
Assessment of systolic volume and cardiac output
- -
Assessment of the repercussions of mechanical ventilation upon the RV
The implementation of hemodynamic monitoring using ultrasound as a tool capable of competing with thermodilution or pulse wave techniques has faced several limitations. At present, ultrasound cannot be regarded as a continuous monitoring tool, though it does constitute an essential exploratory complement. Transesophageal echocardiography devices as small as a nasogastric tube are available on the market and can be kept in place for up to 72h, offering a continuous recording of indixes such as the response to volume replacement therapy based on the distensibility of the superior vena cava (SVC) and ventricular function in visual mode65,66 (Figure S6, Supplementary material).67
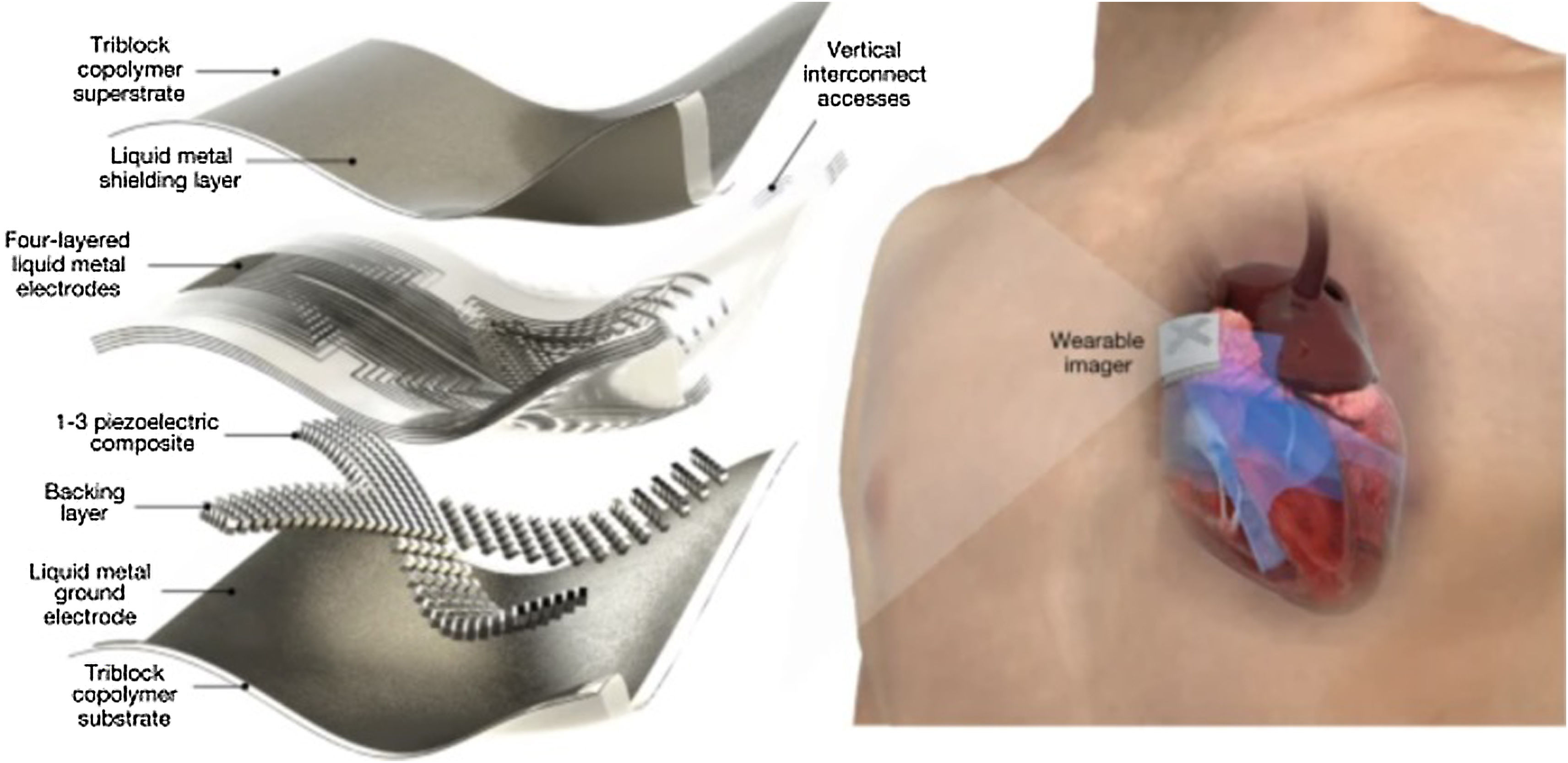
Future developments could include patches adhered to the skin and capable of transmitting images continuously for 48h. A research line at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has produced a patch with the size of a stamp that generates high-resolution images in vivo.68–71 The patch measures approximately 4cm in width and 0.5cm in thickness (Fig. 6),72 and could replace the existing bulky ultrasound systems. Through ultrasound pulses, these devices capture high-resolution images of arterial flow and of the heart cavities, with a wireless signal transmission. In different studies and tests in healthy volunteers, the patches were seen to adapt well to the skin, making it possible to capture images even when standing up or sitting down, jogging or cycling.
This adhered ultrasound device generates enhanced-resolution images by combining an elastic adhesive layer with a rigid series of transducers (which convert energy from one form to another). In between these components, there is a solid hydrogel that transmits sound waves, and the adhesive layer is composed of two thin elastomer films that prevent dehydration of the hydrogel during a certain period.
In the different tests made, the patches have been used in different areas, including the neck, chest, abdomen and arms (Figure S7, Supplementary material).73 The continuous images of the underlying structures are clear, including the changing diameters and areas of the blood vessels and heart cavities, during periods of up to 48h.74–77
Such software is based not only on artificial intelligence, allowing improved interpretation of the ultrasound images, but also on research into frequency- and ultrasound wave-transmitting materials and gels. Although the future potentials and applications remain to be confirmed, this is a very promising field of research in critical care.
ConclusionsArtificial intelligence as a tool applied to ultrasound is already a reality. Its evolution in the coming years will make the learning process shorter, allowing faster and more automated use of the exploratory technique, and resulting in more precise monitoring and echocardiographic diagnosis.
Progressive incorporation of the technology will be faster than expected, affording more precise and fundamental information to intensivists on an immediate basis and with a shorter learning curve. Likewise, the development of new software applications will make cardiovascular physiology more comprehensible.
Lastly, we should ponder whether clinicians will be able to quickly apply these continuous improvements in software applications and their reliability to daily practice, and in which ways the new indixes will change our clinical language. The future is undoubtedly fascinating.
Author contributionsFernando Clau-Terré prepared the manuscript's first draft, which was subsequently modified by the rest of the authors. Fernando Clau-Terré likewise provided the edited videos and images, and requested the permissions for their reproduction.
Financial supportNone.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in relation to the commercial companies cited in the article, and have received no compensations of any kind.
Thanks are due to the authors that have authorized disclosure of the images, and to the companies cited in the article that have permitted to use the teaching materials for understanding the advances in the field.