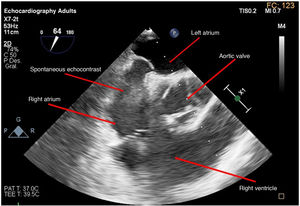
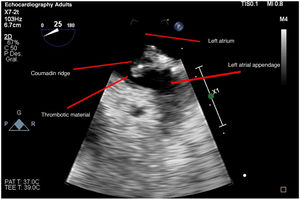
Patient admitted to the ICU due to SARS-CoV-2-induced pneumonia who required mechanical ventilation and was transferred to one of the hospital conventional wards after 14 days at the ICU treated with anticoagulant therapy with enoxaparin. He was readmitted due to respiratory failure. The CAT scan performed revealed the presence of thrombi in segmental arteries of both the right superior and left inferior lobes. The transesophageal echocardiogram performed revealed the presence of dense, spontaneous echocontrast in the right chambers (Appendix B; video 1 and Fig. 1). After the new hospital discharge, the patient showed low level of consciousness. The cranial CAT scan performed revealed the presence of an infarction at right medial cerebral artery level while the transesophageal echocardiogram performed revealed the presence of a coumadin ridge (variant of normality) with attached thrombotic material (Appendix B; video 2 and Fig. 2), and lack of cardiac shunt (Appendix B; video 3). A sequela of left residual hemiparesis remained at the ICU discharge. This is a clear example that the infection due to COVID-19 increases the risk of thromboembolic events.
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more