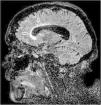
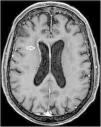
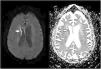
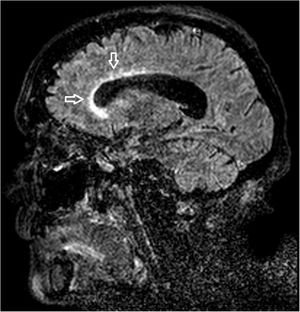
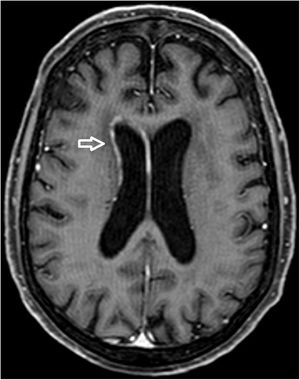
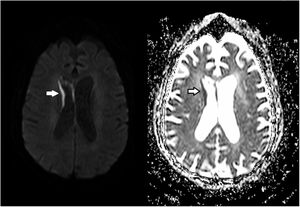
A 68-year-old woman with chronic bronchitis was admitted to the Intensive Care Unit at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic due to respiratory failure and bilateral lung infiltrates consistent with SARS-CoV-2 infection, though PCR testing proved negative on several occasions. During admission she suffered a progressive altered level of consciousness, requiring orotracheal intubation. Aspergillus lentulus was isolated from the bronchial aspirate. Lumbar puncture revealed: glucose 24 mg/dl, total proteins 133.6 mg/dl, leukocytes 136/µl and mononuclear cells > 95%. The brain CT scan showed no acute lesions and the brain MRI study revealed subependymal enhanced signal intensity around the frontal horn and atrioventricular zone of the lateral right ventricle (Figs. 1 and 2), with diffusion restriction in the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) study (Fig. 3). With the suspicion of fungal ventriculitis, PCR testing for Aspergillus spp. was performed in cerebrospinal fluid, with positive results.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare the absence of conflict of interest as reflected in the attached document.
The authors declare that they have not received any financial support. The authors declare that they do not need specific acknowledgments to mention.