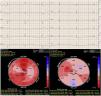
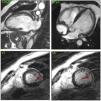
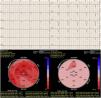
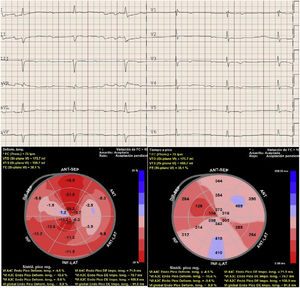
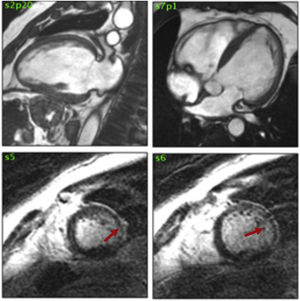
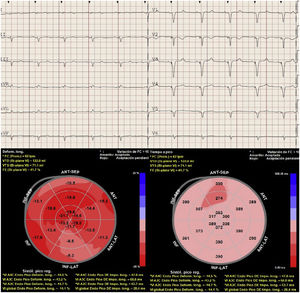
This is the case of a 48-year-old patient with Chagas disease admitted to the ICU with heart failure and 35 bpm bradycardia due to complete AV block with QRS complex of 147 ms and right bundle branch block (Fig. 1). A transient pacemaker was implanted and an echocardiogram was performed (video 1) with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 33% due to global hypokinesis and severely depressed global longitudinal strain (GLS) (−9.9%) with elevated mechanical dispersion of 91 ms (Fig. 1). For all this and due to the cardiac magntic resonance imaging findings that confirmed the presence of biventricular dilatation with LVEF of 33%, and areas of late gadolinium enhancement (Fig. 2), it was decided to implant a cardiac resynchronization therapy device associated with a defibrillator (video 2). Fifteen (15) days after implantation, the patient showed significant functional improvement, ECG with left ventricular pacing with QRS complex of 127 ms (Fig. 3), and an increased LVEF of 48% (video 3) and GLS up to −14% on the echocardiogram with mechanical dispersion reduction of 28.4 msg (Fig. 3).
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more