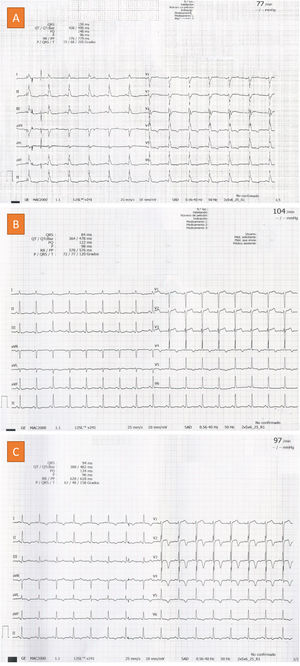
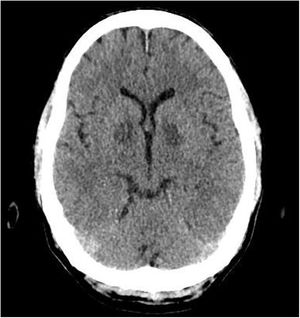
A 53-year-old male was admitted to the Intensive Care Unit with cardiogenic shock secondary to severe carbon monoxide poisoning. Treatment was started with 100% O2 due to initial carboxyhemoglobin levels of 25%. Echocardiography was performed due to sustained hypotension despite resuscitation and vasoactive drugs (Appendix B enclosed video, left), revealing severe biventricular dysfunction with an estimated cardiac output of 1.8 L/min that gradually recovered in the subsequent 48 h with inotropic support in the form of dobutamine (Appendix B enclosed video, right). The initial ECG tracing evidenced no known right bundle block (Fig. 1, image A) that reverted after the first 24 h, evolving towards subendocardial injury on the anterolateral surface and posterior ischemia in those territories (Fig. 1, images B and C). The brain CT scan evidenced symmetrical bilateral hypodensity in the globus pallidus (Fig. 2) – this image being characteristic of carbon monoxide poisoning due to the high iron content and high sensitivity to hypotension.
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more