A 44-year-old male, with history of smoking and alcohol abuse, was admitted to the Intensive Care Unit due to septic shock and sepsis related cardiac dysfunction secondary a pneumococcal community acquired pneumonia.
The patient presented multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, requiring mechanical ventilation, vasopressors, continuous renal replacement therapy and antibiogram-direct antibiotic therapy.
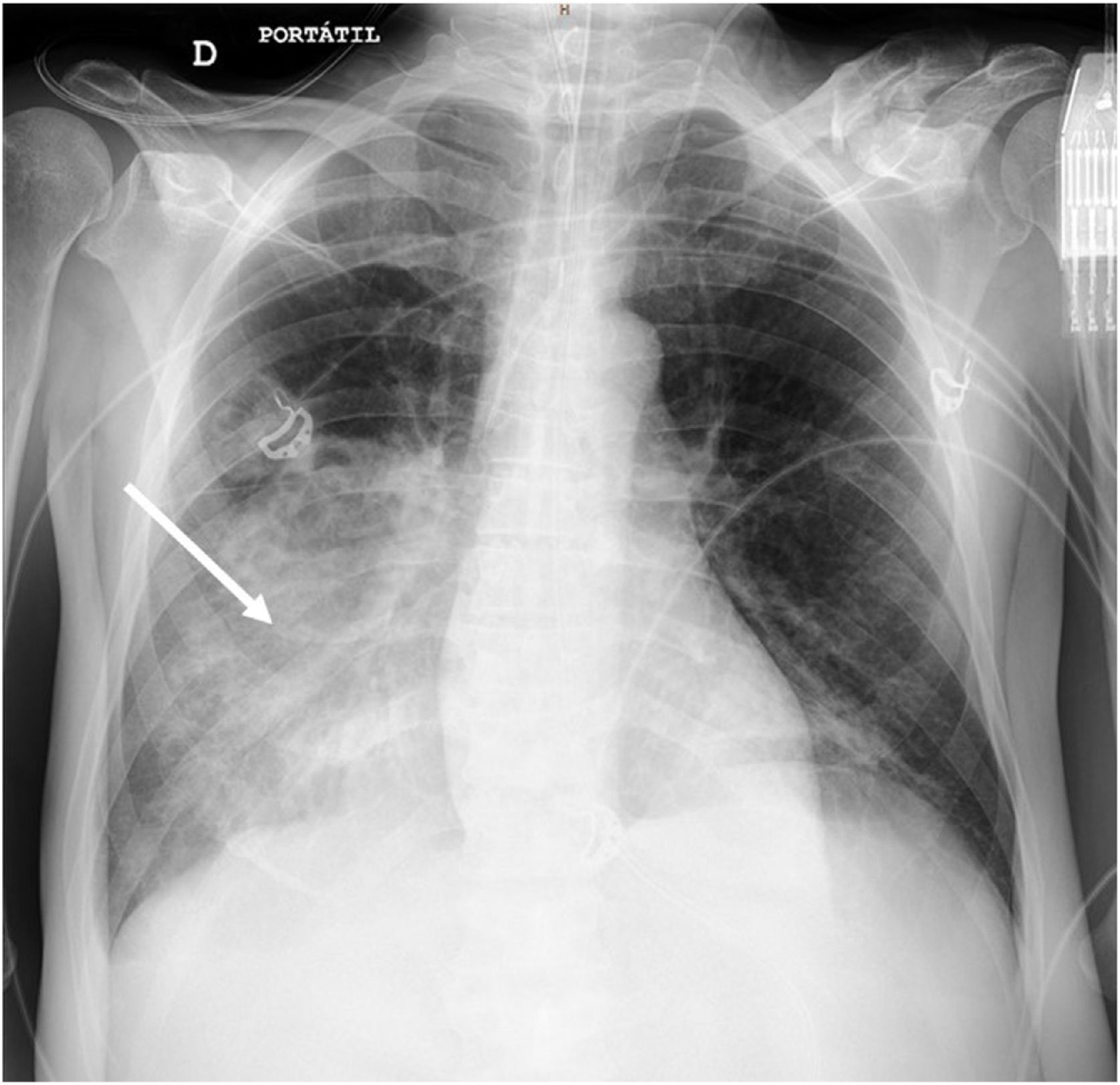
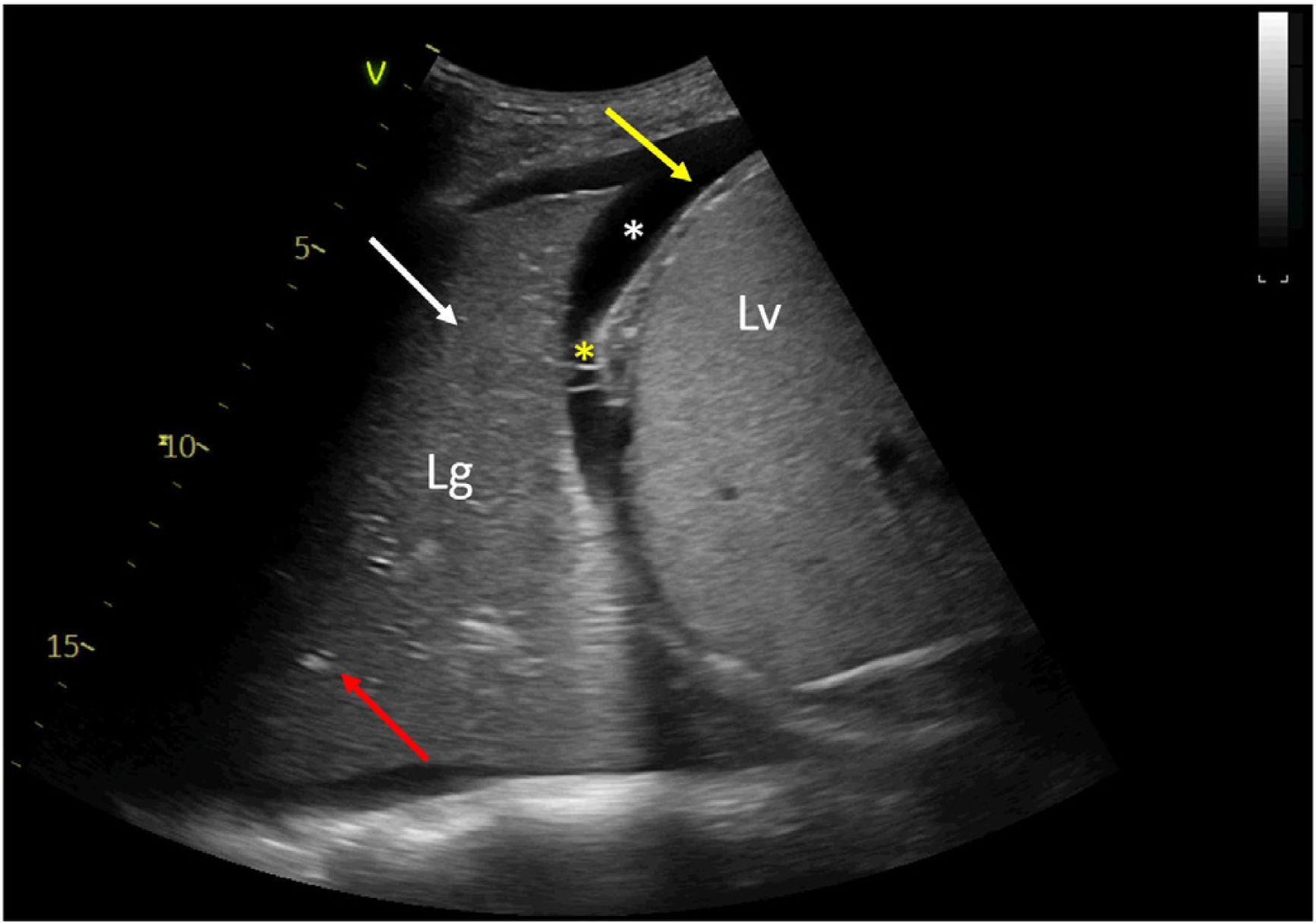
An anteroposterior chest radiography showed an area of lung consolidation in lower right lobe, indicating pneumonia (see Fig. 1). The lung ultrasound showed lobar consolidation, air bronchogram, pleural effusion and fibrin (see Fig. 2), as well as hyperechoic opacities that move centrifugally with respiration (dynamic air bronchogram) (see suppl. material 1). The patient was discharged alive after 2 months.